 Run in Google Colab Run in Google Colab
|
 View source on GitHub View source on GitHub
|
|
Step 3: Smart Sample Selection#
Random sampling wastes labels on redundant near-duplicates. This step uses diversity-based selection to pick high-value scenes that cover your data distribution efficiently.
We’ll use ZCore (Zero-Shot Coreset Selection) to score samples based on:
Coverage: How much of the embedding space does this sample represent?
Redundancy: How many near-duplicates exist?
High ZCore score = valuable for labeling. Low score = redundant, skip it.
Note: For grouped datasets, we compute embeddings on the left camera slice and select at the group level (scene).
[ ]:
import fiftyone as fo
import fiftyone.brain as fob
import numpy as np
from fiftyone import ViewField as F
dataset = fo.load_dataset("annotation_tutorial")
pool = dataset.load_saved_view("pool")
# Get pool groups (scenes)
pool_groups = pool.distinct("group.id")
print(f"Pool: {len(pool_groups)} groups (scenes)")
total_samples = sum(len(pool.select_group_slices([s])) for s in dataset.group_slices)
print(f"Pool: {total_samples} total samples (all slices)")
Compute Embeddings on Left Camera Slice#
For diversity selection, we need embeddings. We compute them on the left camera images since that is our primary 2D annotation target.
Dependencies: This step requires
torchandumap-learn. Install them if needed:pip install torch torchvision umap-learn
[ ]:
# Get left camera slice from pool
pool_left = pool.select_group_slices(["left"])
print(f"Left camera samples in pool: {len(pool_left)}")
[ ]:
# Compute embeddings (takes a few minutes)
fob.compute_visualization(
pool_left,
embeddings="embeddings",
brain_key="img_viz",
verbose=True
)
print("Embeddings computed on left camera slice.")
ZCore: Zero-Shot Coreset Selection#
ZCore scores each sample by iteratively:
Sampling random points in embedding space
Finding the nearest data point (coverage bonus)
Penalizing nearby neighbors (redundancy penalty)
The result: samples covering unique regions score high; redundant samples score low.
[ ]:
def zcore_score(embeddings, n_sample=10000, sample_dim=2, redund_nn=100, redund_exp=4, seed=42):
"""
Compute ZCore scores for coverage-based sample selection.
Reference implementation from https://github.com/voxel51/zcore
Args:
embeddings: np.array of shape (n_samples, embedding_dim)
n_sample: Number of random samples to draw
sample_dim: Number of dimensions to sample at a time
redund_nn: Number of nearest neighbors for redundancy penalty
redund_exp: Exponent for distance-based redundancy penalty
seed: Random seed for reproducibility
Returns:
Normalized scores (0-1) where higher = more valuable for labeling
"""
np.random.seed(seed)
n = len(embeddings)
n_dim = embeddings.shape[1]
emb_min = np.min(embeddings, axis=0)
emb_max = np.max(embeddings, axis=0)
emb_med = np.median(embeddings, axis=0)
scores = np.random.uniform(0, 1, n)
for i in range(n_sample):
if i % 2000 == 0:
print(f" ZCore progress: {i}/{n_sample}")
dim = np.random.choice(n_dim, min(sample_dim, n_dim), replace=False)
sample = np.random.triangular(emb_min[dim], emb_med[dim], emb_max[dim])
embed_dist = np.sum(np.abs(embeddings[:, dim] - sample), axis=1)
idx = np.argmin(embed_dist)
scores[idx] += 1
cover_sample = embeddings[idx, dim]
nn_dist = np.sum(np.abs(embeddings[:, dim] - cover_sample), axis=1)
nn = np.argsort(nn_dist)[1:]
if nn_dist[nn[0]] == 0:
scores[nn[0]] -= 1
else:
nn = nn[:redund_nn]
dist_penalty = 1 / (nn_dist[nn] ** redund_exp + 1e-8)
dist_penalty /= np.sum(dist_penalty)
scores[nn] -= dist_penalty
scores = (scores - np.min(scores)) / (np.max(scores) - np.min(scores) + 1e-8)
return scores.astype(np.float32)
[ ]:
# Get embeddings from left camera samples
pool_left_samples = list(pool_left)
embeddings = np.array([s.embeddings for s in pool_left_samples if s.embeddings is not None])
valid_samples = [s for s in pool_left_samples if s.embeddings is not None]
print(f"Computing ZCore for {len(embeddings)} samples...")
print(f"Embedding dimension: {embeddings.shape[1]}")
[ ]:
# Compute ZCore scores
scores = zcore_score(
embeddings,
n_sample=5000,
sample_dim=2,
redund_nn=50,
redund_exp=4,
seed=42
)
print(f"\nZCore scores computed!")
print(f"Score range: {scores.min():.3f} - {scores.max():.3f}")
[ ]:
# Add ZCore scores to the left camera samples
for sample, score in zip(valid_samples, scores):
sample["zcore"] = float(score)
sample.save()
print(f"Added 'zcore' field to {len(valid_samples)} left camera samples")
Select at the Group Level#
We computed scores on individual samples (left camera), but we need to select groups (scenes). Each group includes all slices (left, right, pcd).
Selection strategy: Use the ZCore score from the left camera sample to rank groups.
[ ]:
# Build group_id -> zcore mapping
group_scores = {}
for sample in valid_samples:
group_id = sample.group.id
group_scores[group_id] = sample.zcore
# Sort groups by ZCore score
sorted_groups = sorted(group_scores.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
print(f"Groups with ZCore scores: {len(sorted_groups)}")
print(f"Top 5 groups by ZCore:")
for gid, score in sorted_groups[:5]:
print(f" {gid[:8]}...: {score:.3f}")
[ ]:
# Select top groups for batch v0
# ~25% of pool groups, minimum 20
batch_size = max(20, int(0.25 * len(sorted_groups)))
selected_group_ids = [gid for gid, _ in sorted_groups[:batch_size]]
print(f"Selected {len(selected_group_ids)} groups for Batch v0")
[ ]:
# Tag ALL samples in selected groups (all slices)
# Must iterate all slices since F("group.id").is_in() does not work on grouped datasets
for slice_name in dataset.group_slices:
view = dataset.select_group_slices([slice_name])
for sample in view.iter_samples(autosave=True):
if sample.group.id in selected_group_ids:
sample.tags.append("batch:v0")
sample.tags.append("to_annotate")
sample["annotation_status"] = "selected"
# Save as view
dataset.save_view("batch_v0", dataset.match_tags("batch:v0"))
# Count results
batch_v0_view = dataset.load_saved_view("batch_v0")
n_groups = len(batch_v0_view.distinct("group.id"))
n_samples = sum(len(batch_v0_view.select_group_slices([s])) for s in dataset.group_slices)
print(f"\nBatch v0:")
print(f" Groups: {n_groups}")
print(f" Total samples (all slices): {n_samples}")
[ ]:
# Verify: check sample counts per slice
batch_view = dataset.load_saved_view("batch_v0")
for slice_name in dataset.group_slices:
slice_count = len(batch_view.select_group_slices([slice_name]))
print(f" {slice_name}: {slice_count} samples")
[ ]:
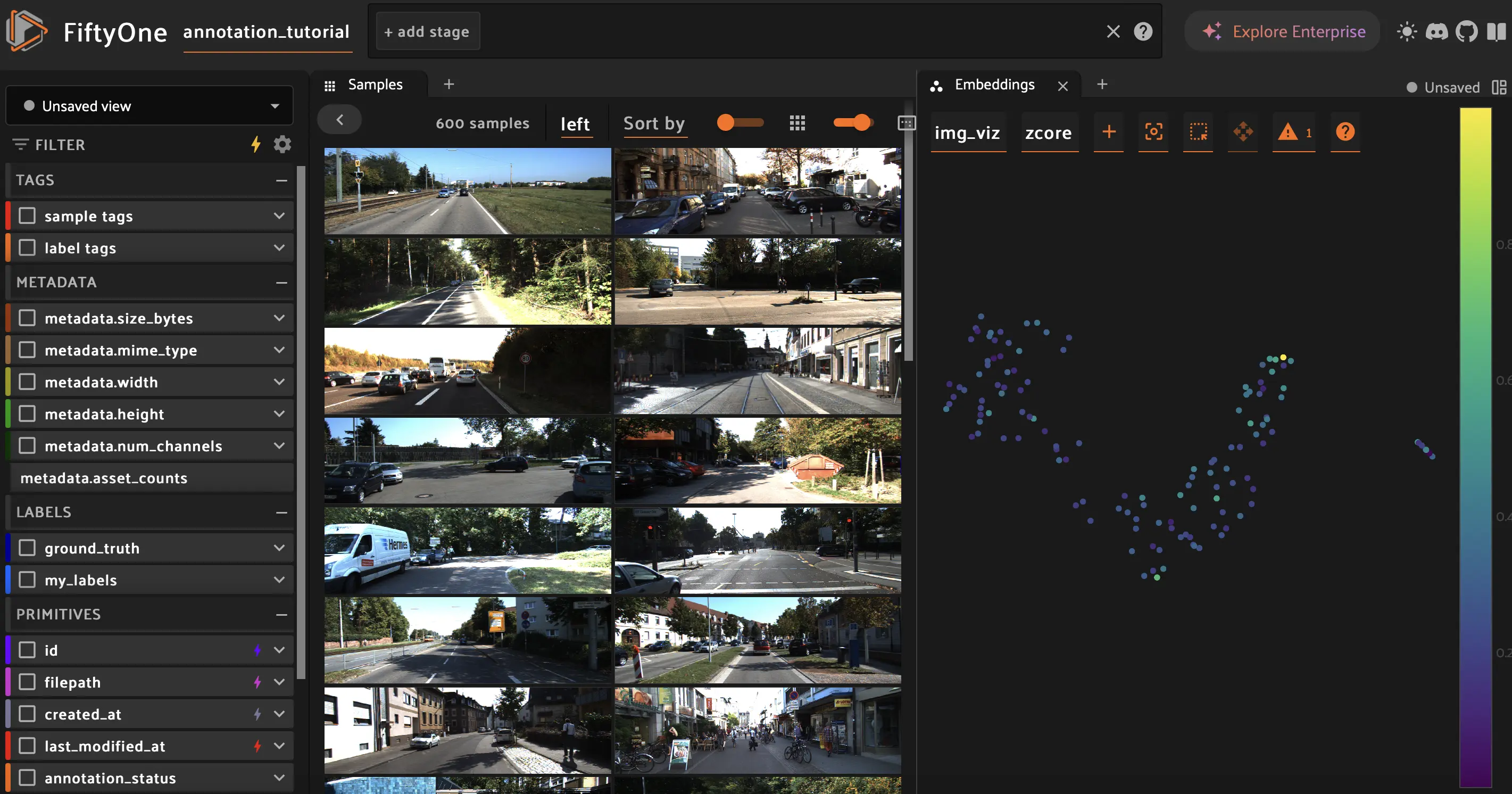
# Visualize in the App
session = fo.launch_app(dataset)
In the App:
Open the Embeddings panel to see the 2D projection
Color by
zcoreto see score distributionFilter by
batch:v0tag to see selected groupsVerify high-ZCore samples are spread across clusters (good coverage)
Why Diversity Sampling Beats Random#
Method |
What it does |
Result |
|---|---|---|
Random |
Picks samples uniformly |
Over-samples dense regions, misses rare cases |
ZCore |
Balances coverage vs redundancy |
Maximizes diversity, fewer wasted labels |
Research shows diversity-based selection can significantly reduce labeling requirements while maintaining model performance.
Summary#
You selected a diverse batch using ZCore:
Computed embeddings on left camera slice
Ran ZCore to score coverage vs redundancy
Selected top-scoring groups (scenes)
Tagged all slices (left, right, pcd) for annotation
Artifacts:
embeddingsfield on left camera sampleszcorefield with selection scoresbatch_v0saved view (all slices for selected groups)Tags:
batch:v0,to_annotate
Next: Step 4 - 2D Annotation + QA