Pinecone Integration#
Pinecone is one of the most popular vector search engines available, and we’ve made it easy to use Pinecone’s vector search capabilities on your computer vision data directly from FiftyOne!
Follow these simple instructions to configure your credentials and get started using Pinecone + FiftyOne.
FiftyOne provides an API to create Pinecone indexes, upload vectors, and run similarity queries, both programmatically in Python and via point-and-click in the App.
Note
Did you know? You can search by natural language using Pinecone similarity indexes!
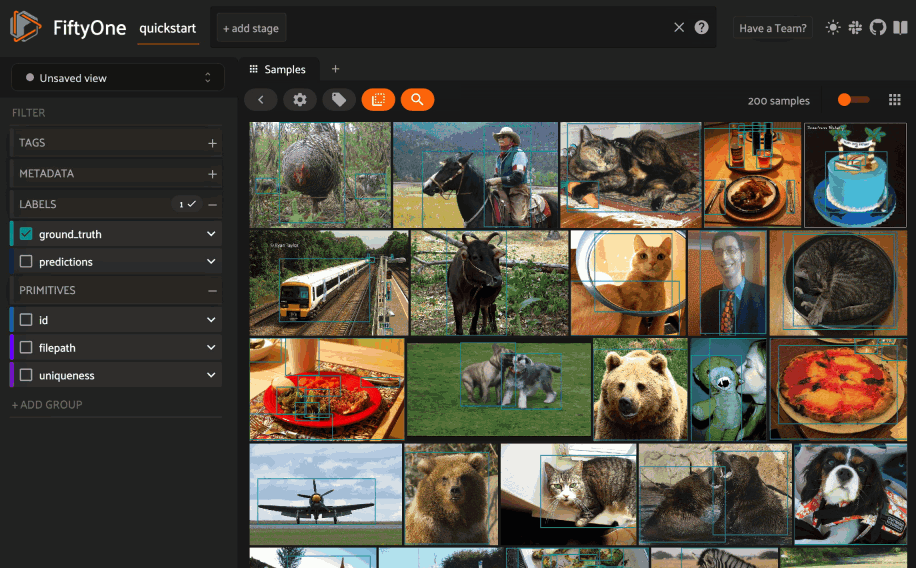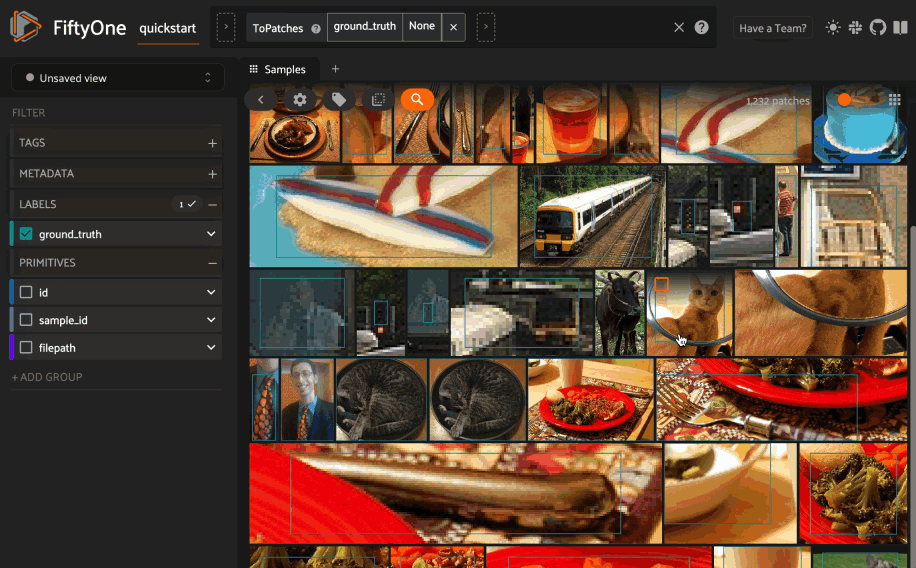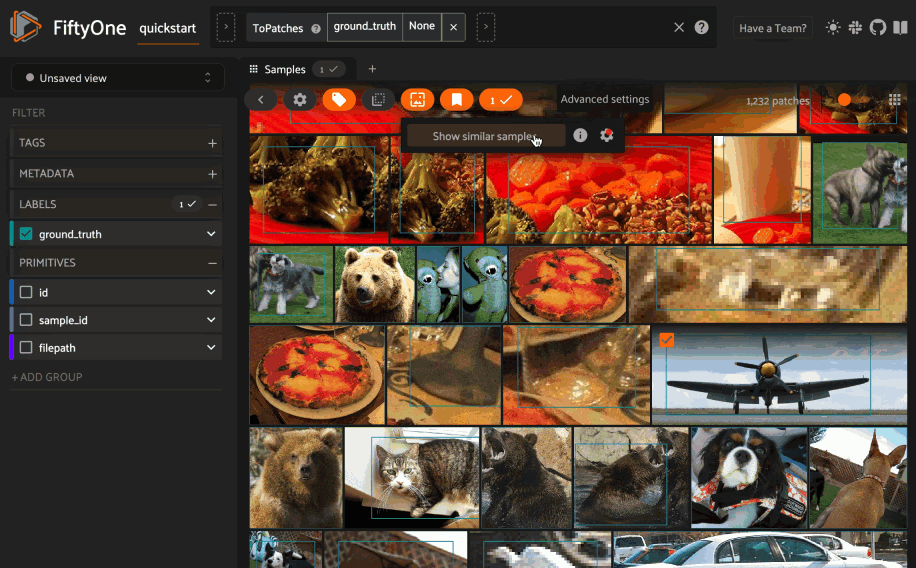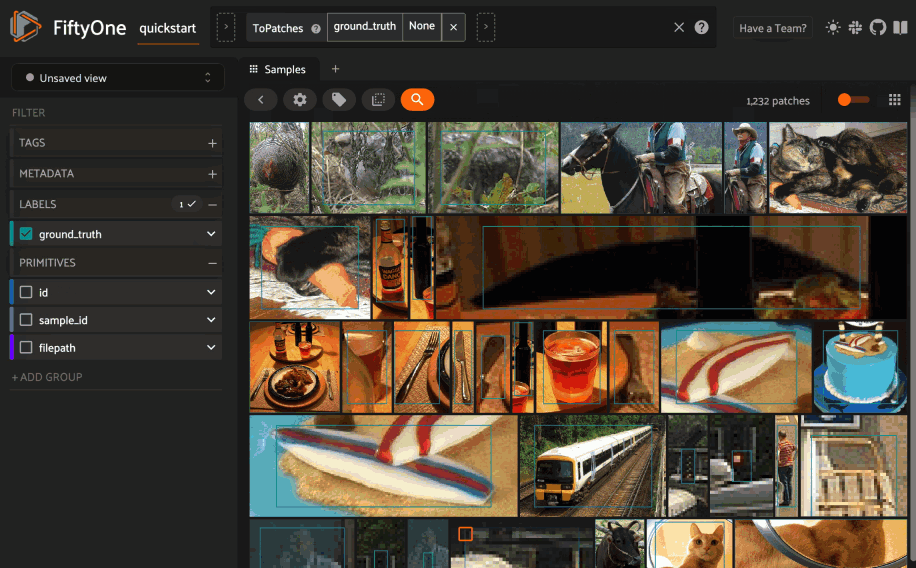
Basic recipe#
The basic workflow to use Pinecone to create a similarity index on your FiftyOne datasets and use this to query your data is as follows:
Load a dataset into FiftyOne
Compute embedding vectors for samples or patches in your dataset, or select a model to use to generate embeddings
Use the
compute_similarity()methodto generate a Pinecone similarity index for the samples or object patches in a dataset by setting the parameterbackend="pinecone"and specifying abrain_keyof your choiceUse this Pinecone similarity index to query your data with
sort_by_similarity()If desired, delete the index
The example below demonstrates this workflow.
Note
You must create a Pinecone account, download a Pinecone API key, and install the Pinecone Python client to run this example:
pip install -U pinecone-client
Note that you can store your Pinecone credentials as described in this section to avoid entering them manually each time you interact with your Pinecone index.
First let’s load a dataset into FiftyOne and compute embeddings for the samples:
1import fiftyone as fo
2import fiftyone.brain as fob
3import fiftyone.zoo as foz
4
5# Step 1: Load your data into FiftyOne
6dataset = foz.load_zoo_dataset("quickstart")
7
8# Steps 2 and 3: Compute embeddings and create a similarity index
9pinecone_index = fob.compute_similarity(
10 dataset,
11 brain_key="pinecone_index",
12 backend="pinecone",
13)
Once the similarity index has been generated, we can query our data in FiftyOne
by specifying the brain_key:
1# Step 4: Query your data
2query = dataset.first().id # query by sample ID
3view = dataset.sort_by_similarity(
4 query,
5 brain_key=brain_key,
6 k=10, # limit to 10 most similar samples
7)
8
9# Step 5 (optional): Cleanup
10
11# Delete the Pinecone index
12pinecone_index = dataset.load_brain_results(brain_key)
13pinecone_index.cleanup()
14
15# Delete run record from FiftyOne
16dataset.delete_brain_run("pinecone_index")
Note
Skip to this section to see a variety of common Pinecone query patterns.
Setup#
The easiest way to get started with Pinecone is to create a free Pinecone account and copy your Pinecone API key.
Installing the Pinecone client#
In order to use the Pinecone backend, you must install the Pinecone Python client:
pip install pinecone-client
Using the Pinecone backend#
By default, calling
compute_similarity() or
sort_by_similarity()
will use an sklearn backend.
To use the Pinecone backend, simply set the optional backend parameter of
compute_similarity() to
"pinecone":
1import fiftyone.brain as fob
2
3fob.compute_similarity(..., backend="pinecone", ...)
Alternatively, you can permanently configure FiftyOne to use the Pinecone backend by setting the following environment variable:
export FIFTYONE_BRAIN_DEFAULT_SIMILARITY_BACKEND=pinecone
or by setting the default_similarity_backend parameter of your
brain config located at ~/.fiftyone/brain_config.json:
{
"default_similarity_backend": "pinecone"
}
Authentication#
In order to connect to a Pinecone server, you must provide your credentials, which can be done in a variety of ways.
Environment variables (recommended)
The recommended way to configure your Pinecone credentials is to store them in the environment variables shown below, which are automatically accessed by FiftyOne whenever a connection to Pinecone is made:
export FIFTYONE_BRAIN_SIMILARITY_PINECONE_API_KEY=XXXXXX
# Serverless indexes
export FIFTYONE_BRAIN_SIMILARITY_PINECONE_CLOUD="aws"
export FIFTYONE_BRAIN_SIMILARITY_PINECONE_REGION="us-east-1"
# Pod-based indexes
export FIFTYONE_BRAIN_SIMILARITY_PINECONE_ENVIRONMENT="us-east-1-aws"
FiftyOne Brain config
You can also store your credentials in your brain config
located at ~/.fiftyone/brain_config.json:
{
"similarity_backends": {
"pinecone": {
"api_key": "XXXXXXXXXXXX",
"cloud": "aws", # serverless indexes
"region": "us-east-1", # serverless indexes
"environment": "us-east-1-aws" # pod-based indexes
}
}
}
Note that this file will not exist until you create it.
Keyword arguments
You can manually provide your Pinecone credentials as keyword arguments each
time you call methods like
compute_similarity() that require
connections to Pinecone:
1import fiftyone.brain as fob
2
3pinecone_index = fob.compute_similarity(
4 ...
5 backend="pinecone",
6 brain_key="pinecone_index",
7 api_key="XXXXXX",
8 cloud="aws",
9 region="us-east-1",
10)
Note that, when using this strategy, you must manually provide the credentials
when loading an index later via
load_brain_results():
1pinecone_index = dataset.load_brain_results(
2 "pinecone_index",
3 api_key="XXXXXX",
4 cloud="aws",
5 region="us-east-1",
6)
Pinecone config parameters#
The Pinecone backend supports a variety of query parameters that can be used to customize your similarity queries. These parameters include:
index_name (None): the name of the Pinecone index to use or create. If not specified, a new unique name is generated automatically
index_type (None): the index type to use when creating a new index. The supported values are
["serverless", "pod"], and the default is"serverless"namespace (None): a namespace under which to store vectors added to the index
metric (“cosine”): the distance/similarity metric to use for the index. Supported values are
("cosine", "dotproduct", "euclidean")replicas (None): an optional number of replicas to use when creating a new pod-based index
shards (None): an optional number of shards to use when creating a new pod-based index
pods (None): an optional number of pods to use when creating a new pod-based index
pod_type (None): an optional pod type to use when creating a new pod-based index
For detailed information on these parameters, see the Pinecone documentation.
You can specify these parameters via any of the strategies described in the previous section. Here’s an example of a brain config that configures a serverless index:
{
"similarity_backends": {
"pinecone": {
"index_name": "your-index",
"index_type": "serverless",
"metric": "cosine",
}
}
}
However, typically these parameters are directly passed to
compute_similarity() to configure
a specific new index:
1pinecone_index = fob.compute_similarity(
2 ...
3 backend="pinecone",
4 brain_key="pinecone_index",
5 index_name="your-index",
6 index_type="serverless",
7 metric="cosine",
8)
Managing brain runs#
FiftyOne provides a variety of methods that you can use to manage brain runs.
For example, you can call
list_brain_runs()
to see the available brain keys on a dataset:
1import fiftyone.brain as fob
2
3# List all brain runs
4dataset.list_brain_runs()
5
6# Only list similarity runs
7dataset.list_brain_runs(type=fob.Similarity)
8
9# Only list specific similarity runs
10dataset.list_brain_runs(
11 type=fob.Similarity,
12 patches_field="ground_truth",
13 supports_prompts=True,
14)
Or, you can use
get_brain_info()
to retrieve information about the configuration of a brain run:
1info = dataset.get_brain_info(brain_key)
2print(info)
Use load_brain_results()
to load the SimilarityIndex instance for a brain run.
You can use
rename_brain_run()
to rename the brain key associated with an existing similarity results run:
1dataset.rename_brain_run(brain_key, new_brain_key)
Finally, you can use
delete_brain_run()
to delete the record of a similarity index computation from your FiftyOne
dataset:
1dataset.delete_brain_run(brain_key)
Note
Calling
delete_brain_run()
only deletes the record of the brain run from your FiftyOne dataset; it
will not delete any associated Pinecone index, which you can do as follows:
# Delete the Pinecone index
pinecone_index = dataset.load_brain_results(brain_key)
pinecone_index.cleanup()
Examples#
This section demonstrates how to perform some common vector search workflows on a FiftyOne dataset using the Pinecone backend.
Note
All of the examples below assume you have configured your Pinecone API key as described in this section.
Create a similarity index#
In order to create a new Pinecone similarity index, you need to specify either
the embeddings or model argument to
compute_similarity(). Here’s a few
possibilities:
1import fiftyone as fo
2import fiftyone.brain as fob
3import fiftyone.zoo as foz
4
5dataset = foz.load_zoo_dataset("quickstart")
6model_name = "clip-vit-base32-torch"
7model = foz.load_zoo_model(model_name)
8brain_key = "pinecone_index"
9
10# Option 1: Compute embeddings on the fly from model name
11fob.compute_similarity(
12 dataset,
13 model=model_name,
14 backend="pinecone",
15 brain_key=brain_key,
16)
17
18# Option 2: Compute embeddings on the fly from model instance
19fob.compute_similarity(
20 dataset,
21 model=model,
22 backend="pinecone",
23 brain_key=brain_key,
24)
25
26# Option 3: Pass precomputed embeddings as a numpy array
27embeddings = dataset.compute_embeddings(model)
28fob.compute_similarity(
29 dataset,
30 embeddings=embeddings,
31 backend="pinecone",
32 brain_key=brain_key,
33)
34
35# Option 4: Pass precomputed embeddings by field name
36dataset.compute_embeddings(model, embeddings_field="embeddings")
37fob.compute_similarity(
38 dataset,
39 embeddings="embeddings",
40 backend="pinecone",
41 brain_key=brain_key,
42)
Note
You can customize the Pinecone index by passing any supported parameters as extra kwargs.
Create a patch similarity index#
You can also create a similarity index for
object patches within your dataset by
specifying a patches_field argument to
compute_similarity():
1import fiftyone as fo
2import fiftyone.brain as fob
3import fiftyone.zoo as foz
4
5dataset = foz.load_zoo_dataset("quickstart")
6
7fob.compute_similarity(
8 dataset,
9 patches_field="ground_truth",
10 model="clip-vit-base32-torch",
11 backend="pinecone",
12 brain_key="pinecone_patches",
13)
Note
You can customize the Pinecone index by passing any supported parameters as extra kwargs.
Connect to an existing index#
If you have already created a Pinecone index storing the embedding vectors for
the samples or patches in your dataset, you can connect to it by passing the
index_name to
compute_similarity():
1import fiftyone as fo
2import fiftyone.brain as fob
3import fiftyone.zoo as foz
4
5dataset = foz.load_zoo_dataset("quickstart")
6
7fob.compute_similarity(
8 dataset,
9 model="clip-vit-base32-torch", # zoo model used (if applicable)
10 embeddings=False, # don't compute embeddings
11 index_name="your-index", # the existing Pinecone index
12 brain_key="pinecone_index",
13 backend="pinecone",
14)
Add/remove embeddings from an index#
You can use
add_to_index()
and
remove_from_index()
to add and remove embeddings from an existing Pinecone index.
These methods can come in handy if you modify your FiftyOne dataset and need to update the Pinecone index to reflect these changes:
1import numpy as np
2
3import fiftyone as fo
4import fiftyone.brain as fob
5import fiftyone.zoo as foz
6
7dataset = foz.load_zoo_dataset("quickstart")
8
9pinecone_index = fob.compute_similarity(
10 dataset,
11 model="clip-vit-base32-torch",
12 brain_key="pinecone_index",
13 backend="pinecone",
14)
15print(pinecone_index.total_index_size) # 200
16
17view = dataset.take(10)
18ids = view.values("id")
19
20# Delete 10 samples from a dataset
21dataset.delete_samples(view)
22
23# Delete the corresponding vectors from the index
24pinecone_index.remove_from_index(sample_ids=ids)
25
26# Add 20 samples to a dataset
27samples = [fo.Sample(filepath="tmp%d.jpg" % i) for i in range(20)]
28sample_ids = dataset.add_samples(samples)
29
30# Add corresponding embeddings to the index
31embeddings = np.random.rand(20, 512)
32pinecone_index.add_to_index(embeddings, sample_ids)
33
34print(pinecone_index.total_index_size) # 210
Retrieve embeddings from an index#
You can use
get_embeddings()
to retrieve embeddings from a Pinecone index by ID:
1import fiftyone as fo
2import fiftyone.brain as fob
3import fiftyone.zoo as foz
4
5dataset = foz.load_zoo_dataset("quickstart")
6
7pinecone_index = fob.compute_similarity(
8 dataset,
9 model="clip-vit-base32-torch",
10 brain_key="pinecone_index",
11 backend="pinecone",
12)
13
14# Retrieve embeddings for the entire dataset
15ids = dataset.values("id")
16embeddings, sample_ids, _ = pinecone_index.get_embeddings(sample_ids=ids)
17print(embeddings.shape) # (200, 512)
18print(sample_ids.shape) # (200,)
19
20# Retrieve embeddings for a view
21ids = dataset.take(10).values("id")
22embeddings, sample_ids, _ = pinecone_index.get_embeddings(sample_ids=ids)
23print(embeddings.shape) # (10, 512)
24print(sample_ids.shape) # (10,)
Querying a Pinecone index#
You can query a Pinecone index by appending a
sort_by_similarity()
stage to any dataset or view. The query can be any of the following:
An ID (sample or patch)
A query vector of same dimension as the index
A list of IDs (samples or patches)
A text prompt (if supported by the model)
1import numpy as np
2
3import fiftyone as fo
4import fiftyone.brain as fob
5import fiftyone.zoo as foz
6
7dataset = foz.load_zoo_dataset("quickstart")
8
9fob.compute_similarity(
10 dataset,
11 model="clip-vit-base32-torch",
12 brain_key="pinecone_index",
13 backend="pinecone",
14)
15
16# Query by vector
17query = np.random.rand(512) # matches the dimension of CLIP embeddings
18view = dataset.sort_by_similarity(query, k=10, brain_key="pinecone_index")
19
20# Query by sample ID
21query = dataset.first().id
22view = dataset.sort_by_similarity(query, k=10, brain_key="pinecone_index")
23
24# Query by a list of IDs
25query = [dataset.first().id, dataset.last().id]
26view = dataset.sort_by_similarity(query, k=10, brain_key="pinecone_index")
27
28# Query by text prompt
29query = "a photo of a dog"
30view = dataset.sort_by_similarity(query, k=10, brain_key="pinecone_index")
Note
Performing a similarity search on a DatasetView will only return
results from the view; if the view contains samples that were not included
in the index, they will never be included in the result.
This means that you can index an entire Dataset once and then perform
searches on subsets of the dataset by
constructing views that contain the images of
interest.
Accessing the Pinecone client#
You can use the index property of a Pinecone index to directly access the
underlying Pinecone client instance and use its methods as desired:
1import fiftyone as fo
2import fiftyone.brain as fob
3import fiftyone.zoo as foz
4
5dataset = foz.load_zoo_dataset("quickstart")
6
7pinecone_index = fob.compute_similarity(
8 dataset,
9 model="clip-vit-base32-torch",
10 brain_key="pinecone_index",
11 backend="pinecone",
12)
13
14print(pinecone_index.index)
Advanced usage#
As previously mentioned, you can customize
your Pinecone indexes by providing optional parameters to
compute_similarity().
Here’s an example of creating a similarity index backed by a customized Pinecone index. Just for fun, we’ll specify a custom index name, use dot product similarity, and populate the index for only a subset of our dataset:
1import fiftyone as fo
2import fiftyone.brain as fob
3import fiftyone.zoo as foz
4
5dataset = foz.load_zoo_dataset("quickstart")
6
7# Create a custom Pinecone index
8pinecone_index = fob.compute_similarity(
9 dataset,
10 model="clip-vit-base32-torch",
11 embeddings=False, # we'll add embeddings below
12 metric="dotproduct",
13 brain_key="pinecone_index",
14 backend="pinecone",
15 index_name="custom-pinecone-index",
16)
17
18# Add embeddings for a subset of the dataset
19view = dataset.take(10)
20embeddings, sample_ids, _ = pinecone_index.compute_embeddings(view)
21pinecone_index.add_to_index(embeddings, sample_ids)
22
23print(pinecone_index.index)