Lightning Flash Integration#
We’ve collaborated with the PyTorch Lightning team to make it easy to train Lightning Flash tasks on your FiftyOne datasets and add predictions from your Flash models to your FiftyOne datasets for visualization and analysis, all in just a few lines of code!
The following Flash tasks are supported natively by FiftyOne:
Note
As Lightning Flash adds support for additional computer vision tasks, we’ll roll out native support for them in FiftyOne via this integration!
Setup#
In order to use the Lightning Flash integration, you’ll need to install Flash:
# This integration currently requires these versions explicitly
pip install lightning-flash>=0.7.0dev
pip install pytorch-lightning
Depending on the type of Flash tasks that you intend to use, you will also need to install some package extras:
# Required to use image tasks
pip install 'lightning-flash[image]'
# Required to use video tasks
pip install 'lightning-flash[video]'
You can always proceed without these initially, as you’ll be prompted to install the appropriate extras when you use a feature that requires them.
Model training#
You can easily train or finetune a Flash
Task on your
FiftyOne datasets with just a few lines of code using
Flash’s builtin
DataModule.from_fiftyone()
method, which is implemented for each of the Flash tasks shown below.
The example below finetunes a Flash
image classification task on a
FiftyOne dataset with Classification ground truth labels:
1from itertools import chain
2
3from flash.core.classification import FiftyOneLabelsOutput
4from flash.image import ImageClassificationData, ImageClassifier
5from flash import Trainer
6
7import fiftyone as fo
8import fiftyone.utils.random as four
9import fiftyone.zoo as foz
10
11# 1 Load your FiftyOne dataset
12dataset = foz.load_zoo_dataset(
13 "cifar10", split="test", max_samples=300
14)
15dataset.untag_samples("test")
16
17# Create splits from the dataset
18splits = {"train": 0.7, "test": 0.1, "val": 0.1, "pred": 0.1}
19four.random_split(dataset, splits)
20
21# Here we use views into one dataset,
22# but you can also use a different dataset for each split
23train_dataset = dataset.match_tags("train")
24test_dataset = dataset.match_tags("test")
25val_dataset = dataset.match_tags("val")
26predict_dataset = dataset.match_tags("pred")
27
28# 2 Create the Datamodule
29datamodule = ImageClassificationData.from_fiftyone(
30 train_dataset=train_dataset,
31 test_dataset=test_dataset,
32 val_dataset=val_dataset,
33 predict_dataset=predict_dataset,
34 label_field="ground_truth",
35 batch_size=4,
36 num_workers=4,
37)
38
39# 3 Build the model
40model = ImageClassifier(
41 backbone="resnet18",
42 labels=datamodule.labels,
43)
44
45# 4 Create the trainer
46trainer = Trainer(
47 max_epochs=1, limit_train_batches=10, limit_val_batches=10,
48)
49
50# 5 Finetune the model
51trainer.finetune(model, datamodule=datamodule)
52
53# 6 Save it!
54trainer.save_checkpoint("/tmp/image_classification_model.pt")
55
56# 7 Generate predictions
57predictions = trainer.predict(
58 model,
59 datamodule=datamodule,
60 output=FiftyOneLabelsOutput(labels=datamodule.labels),
61)
62predictions = list(chain.from_iterable(predictions)) # flatten batches
63
64# Map filepaths to predictions
65predictions = {p["filepath"]: p["predictions"] for p in predictions}
66
67# Add predictions to FiftyOne dataset
68predict_dataset.set_values(
69 "flash_predictions", predictions, key_field="filepath",
70)
71
72# 8 Analyze predictions in the App
73session = fo.launch_app(predict_dataset)
This example below finetunes a Flash
object detection task on a FiftyOne
dataset with Detections ground truth labels:
1from itertools import chain
2
3from flash import Trainer
4from flash.image import ObjectDetectionData, ObjectDetector
5from flash.image.detection.output import FiftyOneDetectionLabelsOutput
6
7import fiftyone as fo
8import fiftyone.utils.random as four
9import fiftyone.zoo as foz
10
11# 1 Load your FiftyOne dataset
12dataset = foz.load_zoo_dataset(
13 "coco-2017",
14 split="validation",
15 max_samples=100,
16 classes=["person"],
17)
18
19# Create splits from the dataset
20splits = {"train": 0.7, "test": 0.1, "val": 0.1}
21four.random_split(dataset, splits)
22
23# Here we use views into one dataset,
24# but you can also use a different dataset for each split
25train_dataset = dataset.match_tags("train")
26test_dataset = dataset.match_tags("test")
27val_dataset = dataset.match_tags("val")
28predict_dataset = train_dataset.take(5)
29
30# Remove background class, it gets added by datamodule
31dataset.default_classes.pop(0)
32
33# 2 Create the Datamodule
34datamodule = ObjectDetectionData.from_fiftyone(
35 train_dataset=train_dataset,
36 test_dataset=test_dataset,
37 val_dataset=val_dataset,
38 predict_dataset=predict_dataset,
39 label_field="ground_truth",
40 transform_kwargs={"image_size": 512},
41 batch_size=4,
42)
43
44# 3 Build the model
45model = ObjectDetector(
46 head="efficientdet",
47 backbone="d0",
48 num_classes=datamodule.num_classes,
49 image_size=512,
50)
51
52# 4 Create the trainer
53trainer = Trainer(max_epochs=1, limit_train_batches=10)
54
55# 5 Finetune the model
56trainer.finetune(model, datamodule=datamodule, strategy="freeze")
57
58# 6 Save it!
59trainer.save_checkpoint("/tmp/object_detection_model.pt")
60
61# 7 Generate predictions
62predictions = trainer.predict(
63 model,
64 datamodule=datamodule,
65 output=FiftyOneDetectionLabelsOutput(labels=datamodule.labels),
66)
67predictions = list(chain.from_iterable(predictions)) # flatten batches
68
69# Map filepaths to predictions
70predictions = {p["filepath"]: p["predictions"] for p in predictions}
71
72# Add predictions to FiftyOne dataset
73dataset.set_values(
74 "flash_predictions", predictions, key_field="filepath",
75)
76
77# 8 Analyze predictions in the App
78session = fo.launch_app(predict_dataset)
This example below finetunes a Flash
semantic segmentation task on a
FiftyOne dataset with Segmentation ground truth labels:
1from itertools import chain
2
3from flash import Trainer
4from flash.core.data.utils import download_data
5from flash.image import SemanticSegmentation, SemanticSegmentationData
6from flash.image.segmentation.output import FiftyOneSegmentationLabelsOutput
7
8import fiftyone as fo
9import fiftyone.zoo as foz
10
11# 1 Load your FiftyOne dataset
12
13# source: https://www.kaggle.com/kumaresanmanickavelu/lyft-udacity-challenge
14download_data(
15 "https://github.com/ongchinkiat/LyftPerceptionChallenge/releases/download/v0.1/carla-capture-20180513A.zip",
16 "/tmp/carla_data/",
17)
18
19dataset = fo.Dataset.from_dir(
20 dataset_dir="/tmp/carla_data",
21 dataset_type=fo.types.ImageSegmentationDirectory,
22 data_path="CameraRGB",
23 labels_path="CameraSeg",
24 force_grayscale=True,
25 shuffle=True,
26)
27
28# Just test and val on train dataset for this example
29predict_dataset = dataset.take(5)
30
31# 2 Create the Datamodule
32datamodule = SemanticSegmentationData.from_fiftyone(
33 train_dataset=dataset,
34 test_dataset=dataset,
35 val_dataset=dataset,
36 predict_dataset=predict_dataset,
37 label_field="ground_truth",
38 transform_kwargs=dict(image_size=(256, 256)),
39 num_classes=21,
40 batch_size=4,
41)
42
43# 3 Build the model
44model = SemanticSegmentation(
45 backbone="mobilenetv3_large_100",
46 head="fpn",
47 num_classes=datamodule.num_classes,
48)
49
50# 4 Create the trainer
51trainer = Trainer(
52 max_epochs=1, limit_train_batches=10, limit_val_batches=5
53)
54
55# 5 Finetune the model
56trainer.finetune(model, datamodule=datamodule, strategy="freeze")
57
58# 6 Save it!
59trainer.save_checkpoint("/tmp/semantic_segmentation_model.pt")
60
61# 7 Generate predictions
62predictions = trainer.predict(
63 model,
64 datamodule=datamodule,
65 output=FiftyOneSegmentationLabelsOutput(),
66)
67predictions = list(chain.from_iterable(predictions)) # flatten batches
68
69# Map filepaths to predictions
70predictions = {p["filepath"]: p["predictions"] for p in predictions}
71
72# Add predictions to FiftyOne dataset
73dataset.set_values(
74 "flash_predictions", predictions, key_field="filepath",
75)
76
77# 8 Analyze predictions in the App
78session = fo.launch_app(predict_dataset)
The example below finetunes a Flash
video classification task on a
FiftyOne dataset with Classification ground truth labels:
1from itertools import chain
2
3from flash.core.classification import FiftyOneLabelsOutput
4from flash import Trainer
5from flash.video import VideoClassificationData, VideoClassifier
6
7import fiftyone as fo
8import fiftyone.utils.random as four
9import fiftyone.zoo as foz
10
11# 1 Load the data
12dataset = foz.load_zoo_dataset(
13 "kinetics-700-2020",
14 split="validation",
15 max_samples=15,
16 shuffle=True,
17)
18dataset.untag_samples("validation")
19
20# Replace spaces in class names with underscore
21labels = dataset.distinct("ground_truth.label")
22labels_map = {l: l.replace(" ", "_") for l in labels}
23dataset = dataset.map_labels("ground_truth", labels_map).clone()
24
25# Get list of labels in dataset
26labels = dataset.distinct("ground_truth.label")
27
28# Create splits from the dataset
29splits = {"train": 0.7, "pred": 0.3}
30four.random_split(dataset, splits)
31
32# Here we use views into one dataset,
33# but you can also use a different dataset for each split
34train_dataset = dataset.match_tags("train")
35predict_dataset = dataset.match_tags("pred")
36
37# 2 Create the Datamodule
38datamodule = VideoClassificationData.from_fiftyone(
39 train_dataset=dataset,
40 predict_dataset=predict_dataset,
41 label_field="ground_truth",
42 batch_size=1,
43 clip_sampler="uniform",
44 clip_duration=1,
45 decode_audio=False,
46)
47
48# 3 Build the model
49model = VideoClassifier(
50 backbone="x3d_xs", labels=datamodule.labels, pretrained=False,
51)
52
53# 4 Create the trainer
54trainer = Trainer(max_epochs=1, limit_train_batches=5)
55
56# 5 Finetune the model
57trainer.finetune(model, datamodule=datamodule, strategy="freeze")
58
59# 6 Save it!
60trainer.save_checkpoint("/tmp/video_classification.pt")
61
62# 7 Generate predictions
63predictions = trainer.predict(
64 model,
65 datamodule=datamodule,
66 output=FiftyOneLabelsOutput(labels=datamodule.labels),
67)
68predictions = list(chain.from_iterable(predictions)) # flatten batches
69
70# Map filepaths to predictions
71predictions = {p["filepath"]: p["predictions"] for p in predictions}
72
73# Add predictions to FiftyOne dataset
74predict_dataset.set_values(
75 "flash_predictions", predictions, key_field="filepath",
76)
77
78# 8 Analyze predictions in the App
79session = fo.launch_app(predict_dataset)
Model predictions#
Once you have a trained Flash task, you can add model predictions to a FiftyOne
Dataset or DatasetView in just a few lines of code using either of the
patterns below.
Applying Flash models to FiftyOne datasets#
The easiest way to generate predictions on a FiftyOne Dataset or
DatasetView with a Flash model is to use the
builtin apply_model()
function, which natively accepts Flash models of any
supported type.
Behind the scenes, FiftyOne will construct the appropriate Flash
Trainer and FiftyOne-style
Output to perform the
inference and output the predictions as Label instances that are added to
your dataset.
1from flash.core.classification import FiftyOneLabelsOutput
2from flash.image import ImageClassifier, ObjectDetector
3
4import fiftyone as fo
5import fiftyone.zoo as foz
6
7# Load your dataset
8dataset = foz.load_zoo_dataset("quickstart", max_samples=5)
9num_classes = len(dataset.distinct("ground_truth.detections.label"))
10
11# Load your Flash model
12cls_model = ImageClassifier(
13 backbone="resnet18", num_classes=num_classes
14)
15
16det_model = ObjectDetector(
17 head="efficientdet",
18 backbone="d0",
19 num_classes=91,
20 image_size=512,
21)
22
23# Predict!
24dataset.apply_model(
25 cls_model, label_field="flash_classifications",
26)
27
28# Some models require transform kwargs that can be pass in
29transform_kwargs = {"image_size": 512}
30dataset.apply_model(
31 det_model,
32 label_field="flash_detections",
33 transform_kwargs=transform_kwargs,
34)
Note
When performing inference with Flash models, you can pass additional
trainer_kwargs in a dictionary like trainer_kwargs={"gpus": 8} to
apply_model(),
which are used to initialize the Flash
Trainer to configure distributed and/or
parallelized inference! See
apply_flash_model()
for more details about supported keyword arguments.
Manually adding predictions#
If you’ve already loaded your datasets into Flash
DataModules without
using FiftyOne, you can still easily use FiftyOne to analyze your model’s
predictions by providing the
Output for the
FiftyOne-style output of the appropriate
type when generating predictions.
Specifying FiftyOne outputs will result in predictions returned as
Label objects that you can easily add to your FiftyOne datasets via
set_values().
1from itertools import chain
2
3from flash import Trainer
4from flash.core.classification import FiftyOneLabelsOutput
5from flash.image import ImageClassificationData, ImageClassifier
6
7import fiftyone as fo
8import fiftyone.zoo as foz
9
10# Load your dataset
11dataset = foz.load_zoo_dataset("quickstart", max_samples=5)
12labels = dataset.distinct("ground_truth.detections.label")
13
14# Load your Flash model
15model = ImageClassifier(labels=labels)
16
17# Create prediction datamodule
18datamodule = ImageClassificationData.from_fiftyone(
19 predict_dataset=dataset,
20 batch_size=1,
21)
22
23# Output FiftyOne format
24output = FiftyOneLabelsOutput(
25 return_filepath=False, labels=labels
26)
27# Predict with trainer
28predictions = Trainer().predict(model, datamodule=datamodule, output=output)
29
30predictions = list(chain.from_iterable(predictions)) # flatten batches
31
32# Predictions is a list of Label objects since ``return_filepath=False``
33# Order corresponds to order of the ``predict_dataset``
34
35# Add predictions to dataset
36dataset.set_values("flash_predictions", predictions)
37
38# Visualize in the App
39session = fo.launch_app(dataset)
Note
FiftyOne outputs have an optional
return_filepath=False
flag that supports returning a list of Label objects corresponding to the
sample ordering of the predict_dataset rather than the default dicts
that contain both the Label objects and the filepath of the
associated media.
Specifying class names#
Generally, Flash model checkpoints will contain the class label strings for the
model. However, if necessary, you can also explicitly pass the labels to most
Output instances,
FiftyOne-style outputs included:
1import fiftyone as fo
2import fiftyone.zoo as foz
3
4from flash import Trainer
5from flash.image import ImageClassificationData, ImageClassifier
6from flash.core.classification import FiftyOneLabelsOutput
7
8# Load your dataset
9dataset = foz.load_zoo_dataset("quickstart", max_samples=5)
10
11datamodule = ImageClassificationData.from_fiftyone(
12 predict_dataset=dataset, batch_size=1
13)
14
15# Load your Flash model
16num_classes = 100
17model = ImageClassifier(backbone="resnet18", num_classes=num_classes)
18
19# Configure output with class labels
20labels = [
21 "label_" + str(i) for i in range(num_classes)
22] # example class labels
23output = FiftyOneLabelsOutput(
24 labels=labels
25) # output FiftyOne format
26
27# Predict with model
28trainer = Trainer()
29predictions = trainer.predict(
30 model, datamodule=datamodule, output=output
31)
32
33predictions = list(chain.from_iterable(predictions)) # flatten batches
34
35# Map filepaths to predictions
36predictions = {p["filepath"]: p["predictions"] for p in predictions}
37
38# Add predictions to dataset
39dataset.set_values(
40 "flash_predictions", predictions, key_field="filepath"
41)
42
43print(dataset.distinct("flash_predictions.label"))
44# ['label_57', 'label_60']
45
46# Visualize in the App
47session = fo.launch_app(dataset)
Image embeddings#
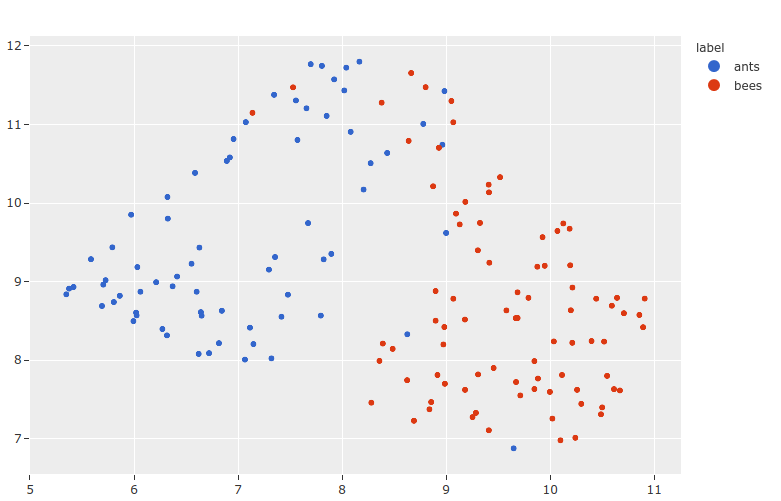
If you use Lightning Flash’s image embeddings tasks to generate feature vectors for your image datasets, then use can easily leverage FiftyOne’s dimensionality reduction and interactive plotting capabilities to visualize your Flash model’s embeddings and execute powerful workflows like cluster analysis and similarity search, all in only a few lines of code!
1import numpy as np
2
3from flash.core.data.utils import download_data
4from flash.image import ImageClassificationData, ImageEmbedder
5from flash import Trainer
6
7import fiftyone as fo
8import fiftyone.brain as fob
9
10# 1 Download data
11download_data(
12 "https://pl-flash-data.s3.amazonaws.com/hymenoptera_data.zip",
13 "/tmp",
14)
15
16# 2 Load data into FiftyOne
17dataset = fo.Dataset.from_dir(
18 "/tmp/hymenoptera_data/test/",
19 fo.types.ImageClassificationDirectoryTree,
20)
21datamodule = ImageClassificationData.from_fiftyone(
22 predict_dataset=dataset,
23 batch_size=1,
24)
25
26# 3 Load model
27embedder = ImageEmbedder(
28 backbone="vision_transformer",
29 training_strategy="barlow_twins",
30 head="barlow_twins_head",
31 pretraining_transform="barlow_twins_transform",
32 training_strategy_kwargs={"latent_embedding_dim": 128},
33 pretraining_transform_kwargs={"size_crops": [32]},
34)
35
36# 4 Generate embeddings
37trainer = Trainer()
38embeddings = trainer.predict(embedder, datamodule=datamodule)
39embeddings = np.stack(sum(embedding_batches, []))
40
41# 5 Visualize images
42session = fo.launch_app(dataset)
43
44# 6 Visualize image embeddings
45results = fob.compute_visualization(dataset, embeddings=embeddings)
46plot = results.visualize(labels="ground_truth.label")
47plot.show()
Note
You can also directly pass your Flash embedding model to
compute_embeddings()
and let FiftyOne handle performing the inference!