Note
This is a community plugin, an external project maintained by its respective author. Community plugins are not part of FiftyOne core and may change independently. Please review each plugin’s documentation and license before use.
Qwen3-VL Video Model for FiftyOne#
A FiftyOne zoo model integration for Qwen3-VL that enables comprehensive video understanding with multiple label types in a single forward pass.
Quick Start#
import fiftyone as fo
import fiftyone.zoo as foz
# Register the model source
foz.register_zoo_model_source(
"https://github.com/harpreetsahota204/qwen3vl_video",
overwrite=True
)
# Load a video dataset
dataset = foz.load_zoo_dataset("quickstart-video", max_samples=5)
dataset.compute_metadata() # Required for temporal/spatial operations
# Load the model (defaults to comprehensive operation)
model = foz.load_zoo_model("Qwen/Qwen3-VL-8B-Instruct")
# Apply to dataset
dataset.apply_model(model, label_field="analysis")
# Or compute embeddings for video similarity
dataset.compute_embeddings(model, embeddings_field="qwen_embeddings")
# Launch the FiftyOne App
session = fo.launch_app(dataset)
Features#
Video Description - Natural language video summaries
⏱ Temporal Event Localization - Events with precise start/end timestamps
Object Tracking - Track objects across frames with bounding boxes
Video OCR - Extract text from frames with spatial locations
Comprehensive Analysis - All of the above in one pass
Video Embeddings - Video-to-video similarity and visualization
Custom Prompts - Full control over model behavior
Supported Models#
Qwen/Qwen3-VL-2B-Instruct(4-6GB VRAM)Qwen/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct(8-12GB VRAM)Qwen/Qwen3-VL-8B-Instruct(16-24GB VRAM) [Recommended]
Operation Modes#
The model supports 6 operation modes, each with a fixed prompt and predictable output format:
1. Comprehensive (Default)#
Analyzes video for all aspects: description, events, objects, scene info, activities.
model = foz.load_zoo_model("Qwen/Qwen3-VL-8B-Instruct")
model.operation = "comprehensive"
dataset.apply_model(model, label_field="analysis")
Output fields:
analysis_summary- Video description (string)analysis_events- Temporal events (fo.TemporalDetections)analysis_objects- Object appearances (fo.TemporalDetections)analysis_scene_info_*- Scene classificationsanalysis_activities_*- Activity classificationssample.frames[N].objects- Frame-level object detectionssample.frames[N].text_content- Frame-level OCR
2. Description#
Simple video description without structured output.
model.operation = "description"
dataset.apply_model(model, label_field="desc")
Output fields:
desc_summary- Plain text description
** Does NOT require metadata**
3. Temporal Localization#
Detects and localizes events in time.
model.operation = "temporal_localization"
dataset.apply_model(model, label_field="events")
Output fields:
events- fo.TemporalDetections with start/end frames
4. Tracking#
Tracks objects across frames with bounding boxes.
model.operation = "tracking"
dataset.apply_model(model, label_field="tracking")
Output fields:
sample.frames[N].objects- fo.Detections per frame
Note: Tracking can be slow and results may vary. Test on a small subset first.
5. OCR#
Extracts text from video frames with bounding boxes.
model.operation = "ocr"
dataset.apply_model(model, label_field="ocr")
Output fields:
sample.frames[N].text_content- fo.Detections with text labels
6. Custom#
Full control over prompts for specialized use cases.
model.operation = "custom"
model.custom_prompt = """Analyze this video and identify:
- Changes in lighting
- Unusual events
- Weather changes
Output in JSON format:
{
"lighting_changes": [{"start": "mm:ss.ff", "end": "mm:ss.ff", "description": "..."}],
"unusual_events": [{"start": "mm:ss.ff", "end": "mm:ss.ff", "description": "..."}],
"weather": [{"start": "mm:ss.ff", "end": "mm:ss.ff", "description": "..."}]
}
Return empty list [] if nothing detected.
"""
dataset.apply_model(model, label_field="custom_analysis")
Output fields:
custom_analysis_result- Raw text output (you post-process as needed)
Custom mode is perfect for:
Domain-specific analysis
Specialized event detection
Custom JSON schemas you’ll parse yourself
Experimenting with prompts
Post-Processing Custom Output#
Custom operation returns raw text, which you can parse into FiftyOne labels:
import fiftyone as fo
import json
import re
from collections import defaultdict
def parse_time_str(timestamp_str):
"""Convert 'mm:ss.ff' timestamp to seconds.
Parses timestamp format and converts to total seconds.
Format: "mm:ss.ff" where mm=minutes, ss=seconds, ff=centiseconds
Args:
timestamp_str: Timestamp string in "mm:ss.ff" format
Returns:
float: Time in seconds, or 0.0 if parsing fails
"""
match = re.match(r'(\d+):(\d+)\.(\d+)', str(timestamp_str))
if not match:
return 0.0
minutes = int(match.group(1))
seconds = int(match.group(2))
centiseconds = int(match.group(3))
return minutes * 60 + seconds + centiseconds / 100.0
def parse_events_to_temporal_detections(events, label, sample):
detections = []
for event in events:
start_sec = parse_time_str(event["start"])
end_sec = parse_time_str(event["end"])
# Use description as the label if available, otherwise use category name
event_label = event.get("description", label)
detection = fo.TemporalDetection.from_timestamps(
[start_sec, end_sec],
label=event_label,
sample=sample
)
detections.append(detection)
return fo.TemporalDetections(detections=detections)
def clean_and_parse_json(text):
"""Remove markdown code blocks and parse JSON"""
text = re.sub(r'```(?:json)?\s*|\s*```', '', text).strip()
return json.loads(text)
# Iterate over all samples and process the 'custom_output_result' field
for sample in dataset.iter_samples(autosave=True):
content_str = sample["custom_output_result"]
events_dict = clean_and_parse_json(content_str)
for category, events in events_dict.items():
if events:
sample[category] = parse_events_to_temporal_detections(events, category, sample)
Example: Parsing as Classifications
For categorical analysis like content rating or sentiment:
model.operation = "custom"
model.custom_prompt = """Analyze this video and provide:
{
"content_type": "educational/entertainment/promotional/other",
"safety_rating": "safe/moderate/unsafe",
"primary_activity": "sports/cooking/gaming/vlog/other"
}
"""
dataset.apply_model(model, label_field="analysis")
# Parse into Classifications
for sample in dataset.iter_samples(autosave=True):
content_str = sample["analysis_result"]
result = clean_and_parse_json(content_str)
# Add as Classifications
sample["content_type"] = fo.Classification(label=result["content_type"])
sample["safety_rating"] = fo.Classification(label=result["safety_rating"])
sample["primary_activity"] = fo.Classification(label=result["primary_activity"])
Video Embeddings#
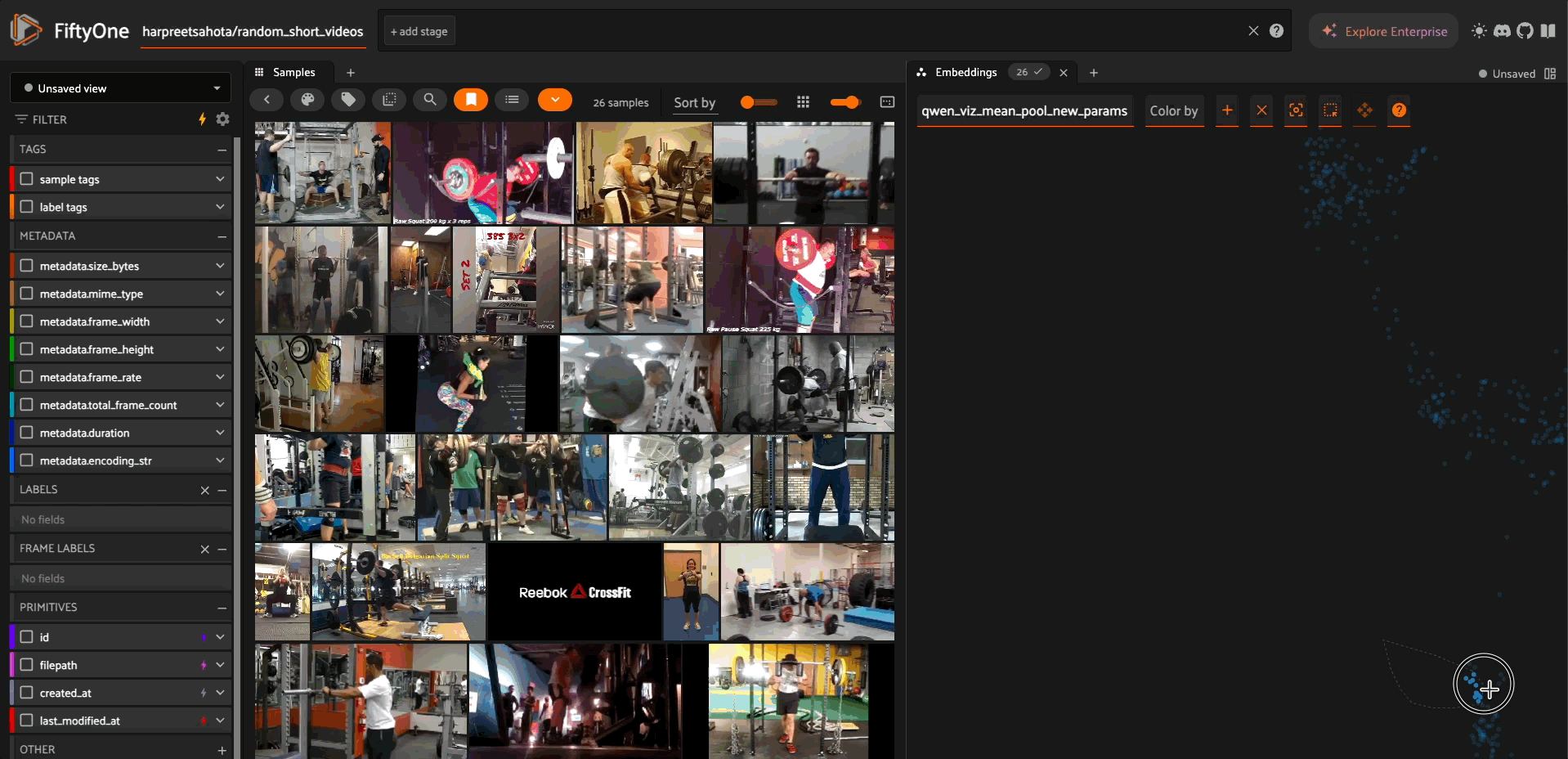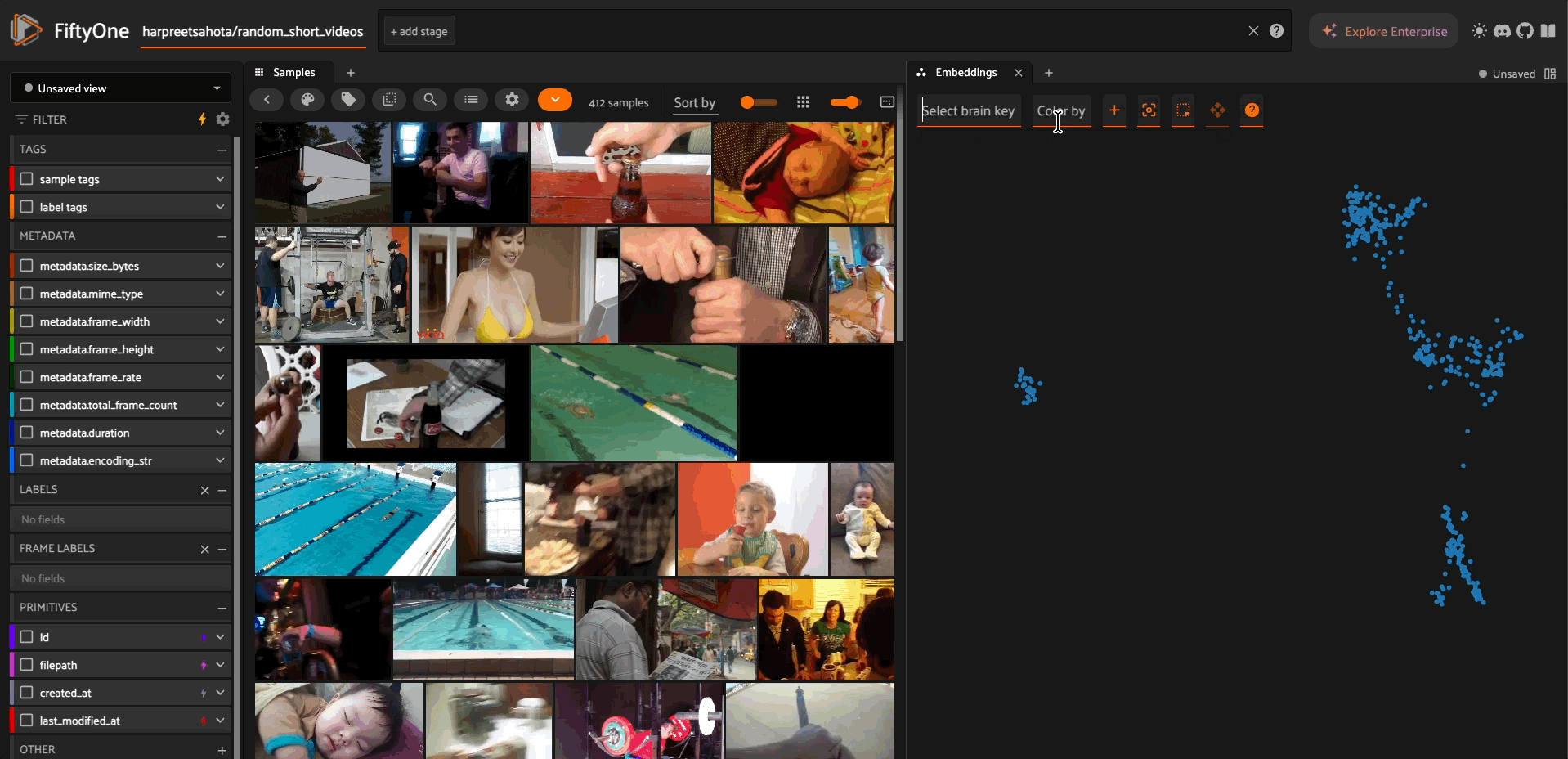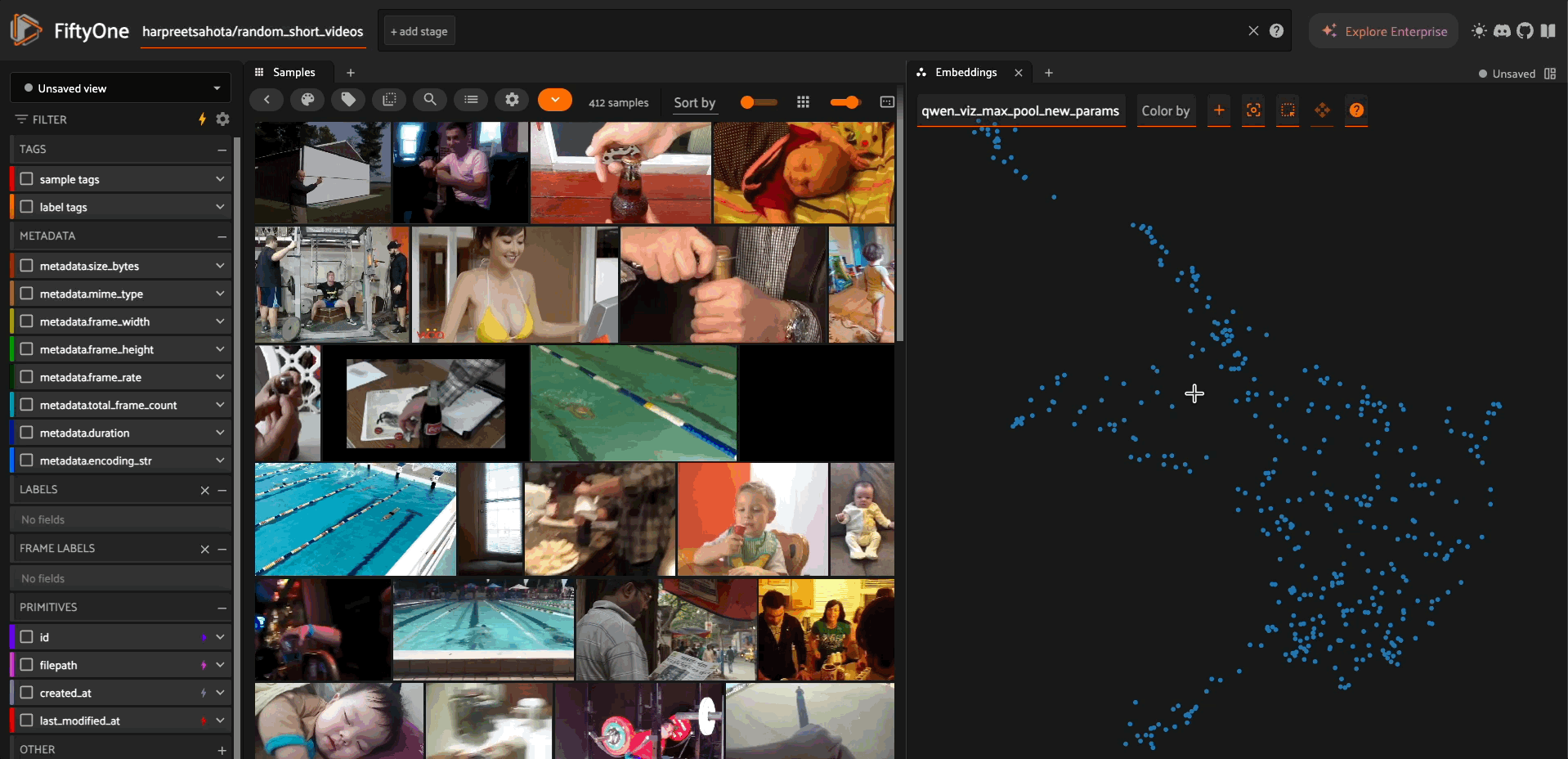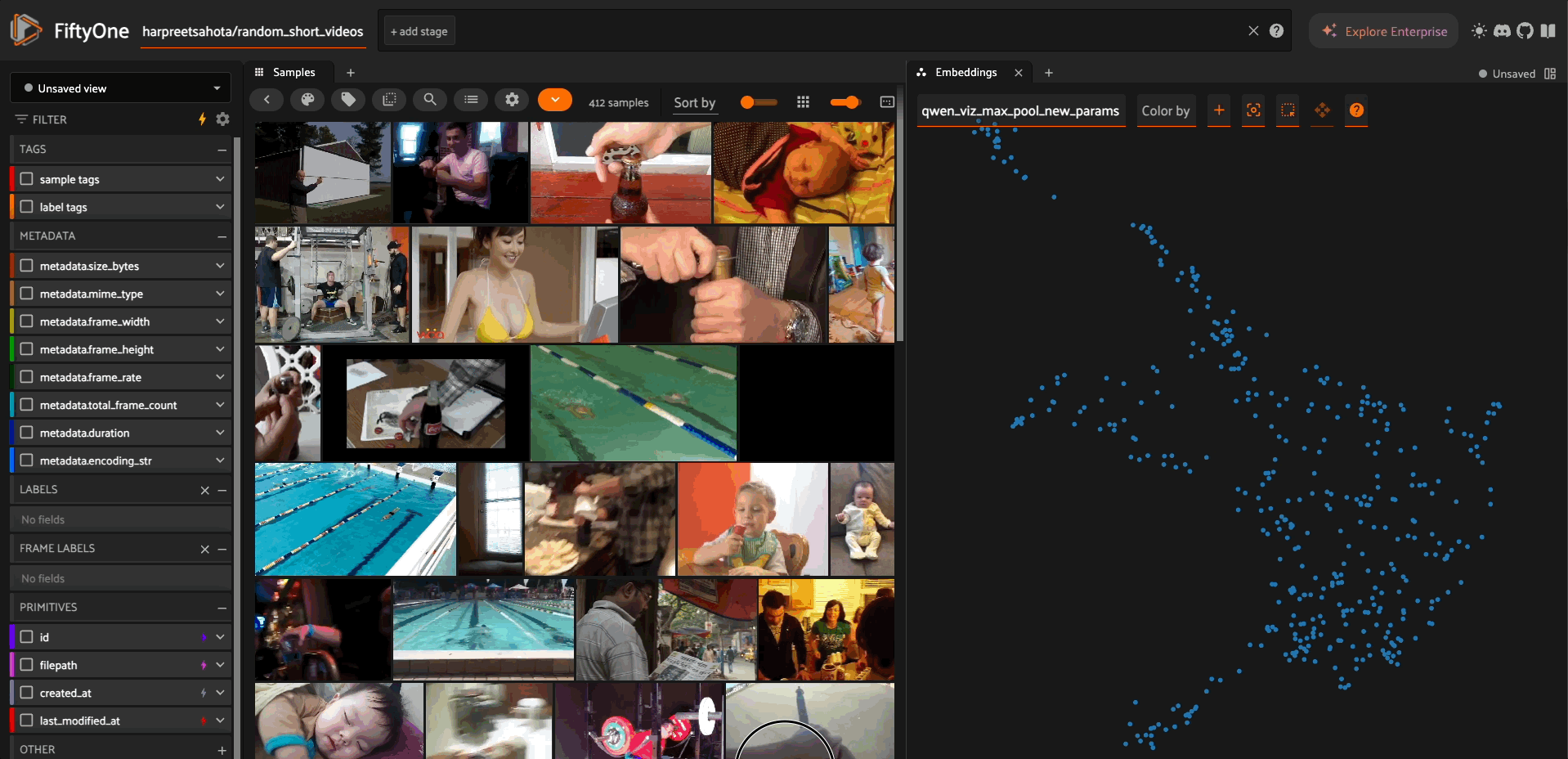
The model supports generating fixed-dimension embeddings for video similarity analysis and visualization.
Basic Usage#
import fiftyone as fo
import fiftyone.zoo as foz
# Load model with pooling strategy
model = foz.load_zoo_model(
"Qwen/Qwen3-VL-8B-Instruct",
pooling_strategy="mean" # Options: "cls", "mean", "max"
)
# Compute embeddings for entire dataset
dataset.compute_embeddings(
model,
embeddings_field="qwen_embeddings",
skip_failures=True
)
Pooling Strategies#
The pooling strategy determines how variable-length video representations are converted to fixed-dimension vectors:
"cls" - Uses the first token (CLS token)
Best for: Following standard BERT-style embeddings
Characteristics: Fast, focused on global context
"mean" - Average pooling across all tokens
Best for: Capturing overall content uniformly
Characteristics: Smooth, balanced representation
"max" - Max pooling across tokens
Best for: Emphasizing salient features
Characteristics: Highlights distinctive elements
# Try different pooling strategies
for strategy in ["cls", "mean", "max"]:
model.pooling_strategy = strategy
dataset.compute_embeddings(
model,
embeddings_field=f"qwen_embeddings_{strategy}"
)
Visualization with UMAP#
Visualize video embeddings in 2D/3D space:
import fiftyone.brain as fob
# Compute UMAP visualization
results = fob.compute_visualization(
dataset,
method="umap", # Also supports "tsne", "pca"
brain_key="qwen_viz",
embeddings="qwen_embeddings",
num_dims=2 # or 3 for 3D
)
# Launch app with visualization
session = fo.launch_app(dataset)
Video-to-Video Similarity#
Find similar videos based on visual content:
import fiftyone.brain as fob
# Build similarity index
fob.compute_similarity(
dataset,
brain_key="qwen_similarity",
embeddings="qwen_embeddings"
)
# Find videos similar to a specific sample
query_sample = dataset.first()
similar_view = dataset.sort_by_similarity(
query_sample,
k=10, # Return 10 most similar videos
brain_key="qwen_similarity"
)
session = fo.launch_app(similar_view)
Important Notes#
Text-to-video search is NOT supported - You can only do video-to-video similarity (find similar videos based on a reference video). Text queries to search videos are not available.
Pooling strategy affects embeddings - Different pooling methods produce different embedding spaces. Experiment to find what works best for your videos.
# Compare different pooling strategies
for strategy in ["cls", "mean", "max"]:
model.pooling_strategy = strategy
dataset.compute_embeddings(
model,
embeddings_field=f"qwen_embeddings_{strategy}"
)
Complete Example#
import fiftyone as fo
import fiftyone.zoo as foz
import fiftyone.brain as fob
from fiftyone.utils.huggingface import load_from_hub
# Load dataset
dataset = load_from_hub(
"harpreetsahota/random_short_videos",
dataset_name="random_short_videos"
)
dataset.compute_metadata()
# Register model source
foz.register_zoo_model_source(
"https://github.com/harpreetsahota204/qwen3vl_video",
overwrite=True
)
# Load model with specific pooling
model = foz.load_zoo_model(
"Qwen/Qwen3-VL-8B-Instruct",
total_pixels=2048*32*32,
max_frames=120,
pooling_strategy="max"
)
# Compute embeddings
dataset.compute_embeddings(
model,
embeddings_field="qwen_embeddings",
skip_failures=True
)
# Visualize with UMAP
fob.compute_visualization(
dataset,
method="umap",
brain_key="qwen_viz",
embeddings="qwen_embeddings",
num_dims=2
)
# Build similarity index
fob.compute_similarity(
dataset,
brain_key="qwen_similarity",
embeddings="qwen_embeddings"
)
# Launch app
session = fo.launch_app(dataset)
Dynamic Reconfiguration#
The model supports dynamic property changes without reloading:
# Load once
model = foz.load_zoo_model("Qwen/Qwen3-VL-8B-Instruct")
# Switch operations (no reload!)
model.operation = "description"
dataset.apply_model(model, label_field="desc")
model.operation = "ocr"
dataset.apply_model(model, label_field="ocr")
model.operation = "temporal_localization"
dataset.apply_model(model, label_field="events")
# Adjust video processing
model.max_frames = 60
model.sample_fps = 5
# Tune generation
model.temperature = 0.9
model.max_new_tokens = 4096
All configurable properties:
# Video processing
model.total_pixels = 2048*32*32
model.min_pixels = 64*32*32
model.max_frames = 120
model.sample_fps = 10
model.image_patch_size = 16
# Text generation
model.max_new_tokens = 8192
model.do_sample = True
model.temperature = 0.7
model.top_p = 0.8
model.top_k = 20
model.repetition_penalty = 1.0
# Operation
model.operation = "comprehensive" # or other modes
model.custom_prompt = "..." # for custom operation
# Embeddings
model.pooling_strategy = "max" # Options: "cls", "mean", "max"
Installation#
Prerequisites#
pip install fiftyone
Model Dependencies#
When you first load the model, FiftyOne will automatically install:
transformers>=4.37.0torchtorchvisionqwen-vl-utilsdecord
Or install manually:
pip install transformers torch torchvision qwen-vl-utils decord
Memory Configuration#
Low Memory (4-6GB VRAM)#
model = foz.load_zoo_model(
"Qwen/Qwen3-VL-2B-Instruct",
total_pixels=5*1024*32*32,
max_frames=32,
sample_fps=0.5
)
Balanced (8-12GB VRAM)#
model = foz.load_zoo_model(
"Qwen/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct",
total_pixels=20*1024*32*32,
max_frames=64,
sample_fps=1
)
High Quality (16-24GB VRAM)#
model = foz.load_zoo_model(
"Qwen/Qwen3-VL-8B-Instruct",
total_pixels=128*1024*32*32,
max_frames=256,
sample_fps=2
)
Important: Metadata Requirement#
Most operations require video metadata for timestamp and frame conversion:
# ALWAYS do this first!
dataset.compute_metadata()
# Then apply model
model = foz.load_zoo_model("Qwen/Qwen3-VL-8B-Instruct")
dataset.apply_model(model, label_field="analysis")
Operations requiring metadata:
comprehensivetemporal_localizationtrackingocr
Operations NOT requiring metadata:
descriptioncustom(if not using temporal features)
Complete Example#
import fiftyone as fo
import fiftyone.zoo as foz
from fiftyone.utils.huggingface import load_from_hub
# Register model source
foz.register_zoo_model_source(
"https://github.com/harpreetsahota204/qwen3vl_video",
overwrite=True
)
# Load dataset
dataset = load_from_hub(
"harpreetsahota/random_short_videos",
dataset_name="random_short_videos"
)
# Compute metadata (required!)
dataset.compute_metadata()
# Load model
model = foz.load_zoo_model("Qwen/Qwen3-VL-8B-Instruct")
# Run comprehensive analysis
model.operation = "comprehensive"
dataset.apply_model(model, label_field="comprehensive", skip_failures=True)
# Add descriptions
model.operation = "description"
dataset.apply_model(model, label_field="desc", skip_failures=True)
# Extract text with OCR
model.operation = "ocr"
dataset.apply_model(model, label_field="ocr", skip_failures=True)
# Detect temporal events
model.operation = "temporal_localization"
dataset.apply_model(model, label_field="events", skip_failures=True)
# Custom analysis
model.operation = "custom"
model.custom_prompt = """Analyze for safety concerns:
{
"potential_hazards": [{"start": "mm:ss.ff", "end": "mm:ss.ff", "description": "..."}],
"safety_rating": "low/medium/high"
}
"""
dataset.apply_model(model, label_field="safety", skip_failures=True)
# Launch app
session = fo.launch_app(dataset)
Coordinate System#
Bounding boxes follow FiftyOne’s format:
[x, y, width, height] # All values in [0, 1] relative coordinates
Where:
x= top-left x (fraction of image width)y= top-left y (fraction of image height)width= box width (fraction of image width)height= box height (fraction of image height)
Timestamp Format#
Model outputs use mm:ss.ff format (minutes:seconds.centiseconds).
The integration automatically converts these to frame numbers using video FPS.
Troubleshooting#
“Sample metadata required”#
# Fix: Compute metadata first
dataset.compute_metadata()
Out of memory errors#
# Reduce processing parameters
model.total_pixels = 1024*32*32 # Lower resolution
model.max_frames = 32 # Fewer frames
model.sample_fps = 0.5 # Lower sampling rate
Empty results / No detections#
This is normal! Not all videos contain text (OCR) or trackable objects. The model will create empty label containers instead of raising errors.
Slow inference#
# Use smaller model
model = foz.load_zoo_model("Qwen/Qwen3-VL-2B-Instruct")
# Process fewer frames
model.max_frames = 32
model.sample_fps = 0.5
# Reduce video quality
model.total_pixels = 5*1024*32*32
Advanced: Building Multi-Field Models#
This implementation demonstrates how to create FiftyOne models that add multiple fields in one inference pass:
def predict(self, arg, sample=None):
"""Return dict with mixed sample/frame-level labels"""
return {
# Sample-level (string keys)
"summary": "Video description",
"events": fo.TemporalDetections(detections=[...]),
# Frame-level (integer keys)
1: {"objects": fo.Detections(detections=[...])},
5: {"objects": fo.Detections(detections=[...])}
}
See the source code in zoo.py for a complete reference implementation.
License#
FiftyOne: Apache 2.0
Qwen3-VL: Apache 2.0 (see model card)
This integration: Apache 2.0
Citation#
@article{qwen3vl2024,
title={Qwen3-VL: Towards Versatile Vision-Language Understanding},
author={Qwen Team},
year={2024}
}
@misc{fiftyone2020,
title={FiftyOne},
author={Voxel51},
year={2020},
howpublished={\url{https://fiftyone.ai}}
}
Support & Contributing#
Issues: GitHub Issues
FiftyOne Docs: docs.voxel51.com
FiftyOne Community: Discord
Qwen3-VL: HuggingFace
Acknowledgments#
Built on top of:
FiftyOne by Voxel51
Qwen3-VL by Qwen Team
Transformers by HuggingFace
