Note
This is a community plugin, an external project maintained by its respective author. Community plugins are not part of FiftyOne core and may change independently. Please review each plugin’s documentation and license before use.
Molmo2 - FiftyOne Model Zoo Integration#
Molmo2 is a family of open vision-language models developed by the Allen Institute for AI (Ai2) that support image, video, and multi-image understanding and grounding. Molmo2 models are trained on publicly available third-party datasets and Molmo2 data, a collection of highly-curated image-text and video-text pairs. It has state-of-the-art performance among multimodal models with similar size.
Use Cases#
Molmo2’s core strength is grounding — precise pixel-level localization and tracking over time. While standard models might say “a car passed by,” Molmo2 can point to the exact car, follow it through a crowd, and mark the exact second it crossed a line.
Domain |
Applications |
|---|---|
Robotics & Automation |
Spatial affordance prediction, action counting (“How many times did the robot grasp the block?”), event localization |
Autonomous Driving |
Vehicle tracking, traffic monitoring, pedestrian detection through occlusions |
Sports Analytics |
Athlete tracking, action spotting (goals, fouls), multi-player trajectory analysis |
Document & Business |
Chart/table understanding, multi-image reasoning for policy analysis, administrative workflow automation |
Media & Accessibility |
Dense video captioning (924 words avg), video search metadata, assistive narration for visually impaired |
Generative AI QA |
Localizing visual artifacts in AI-generated videos (vanishing subjects, physical incongruities) |
Model Checkpoints#
Model |
Base LLM |
Vision Backbone |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Olmo3-7B-Instruct |
SigLIP 2 |
Outperforms others on short videos, counting, and captioning |
|
Qwen3-4B-Instruct |
SigLIP 2 |
Compact model with competitive performance |
|
Qwen3-8B |
SigLIP 2 |
Balanced size and performance |
|
Qwen3-4B-Instruct |
SigLIP 2 |
Finetuned on Molmo2-VideoPoint data only for video pointing and counting |
All models are competitive on long-videos.
Installation#
Important: Requires transformers==4.57.1
pip install transformers==4.57.1
pip install fiftyone umap-learn
pip install einops accelerate decord2 molmo_utils
Usage#
Load a Dataset#
import fiftyone as fo
from fiftyone.utils.huggingface import load_from_hub
dataset = load_from_hub(
"Voxel51/qualcomm-interactive-video-dataset",
max_samples=20,
overwrite=True
)
# REQUIRED: Compute metadata (needed for timestamp-to-frame conversion)
dataset.compute_metadata()
Load the Model#
import fiftyone.zoo as foz
model = foz.load_zoo_model("allenai/Molmo2-4B")
Operations#
Operation |
Prompt Template |
Output Field Type |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Frame-level |
|
|
Frame-level |
|
Uses prompt directly |
Sample-level string |
|
Fixed prompt (finds activity events) |
Sample-level |
|
Fixed prompt (full video analysis) |
Sample-level mixed (see below) |
Output Fields by Operation#
pointing / tracking:
Frame-level
fo.Keypointsstored on each frameEach keypoint has
label,points(normalized x, y), andindex(object ID)For tracking, keypoints share
fo.Instanceobjects to link across frames
describe:
Sample-level string field containing the model’s text response
temporal_localization:
Sample-level
fo.TemporalDetectionswithstart/endframe numbers and event descriptions
comprehensive:
summary: Sample-level stringevents:fo.TemporalDetectionsobjects:fo.TemporalDetections(with first/last appearance times)text_content:fo.TemporalDetections(for any text detected in video)scene_info_*:fo.Classificationfields (setting, time_of_day, location_type)activities_*:fo.Classificationorfo.Classificationsfields
Embeddings#
Generate fixed-dimension vector embeddings for each video. Useful for similarity search, clustering, and visualization.
Added field: molmo_embeddings — a numpy array of shape (hidden_dim,) on each sample.
Pooling strategy: Controls how variable-length hidden states are collapsed into a fixed-size vector:
mean(default) — average across all tokensmax— max pooling across tokenscls— use the first (CLS) token only
model.pooling_strategy = "mean" # or "max" or "cls"
dataset.compute_embeddings(
model,
batch_size=8,
num_workers=2,
embeddings_field="molmo_embeddings",
skip_failures=False
)
Visualize Embeddings#
Use FiftyOne Brain to project embeddings into 2D/3D for visualization in the App.
import fiftyone.brain as fob
results = fob.compute_visualization(
dataset,
method="umap", # Also supports "tsne", "pca"
brain_key="molmo_viz",
embeddings="molmo_embeddings",
num_dims=2 # or 3 for 3D
)
Describe#
Generate free-form text descriptions, captions, or answers to questions about videos. The prompt is used directly without any template.
Added field: A string field (e.g., prompted_describe or answer_pred) containing the model’s text response on each sample.
# With a global prompt
model.operation = "describe"
model.prompt = "Provide a short description for what is happening in the video"
dataset.apply_model(
model,
"prompted_describe",
batch_size=16,
num_workers=4,
skip_failures=False
)
# With per-sample prompts from a field (e.g., for VQA)
model.operation = "describe"
dataset.apply_model(
model,
prompt_field="question",
label_field="answer_pred",
batch_size=16,
num_workers=1,
skip_failures=False
)
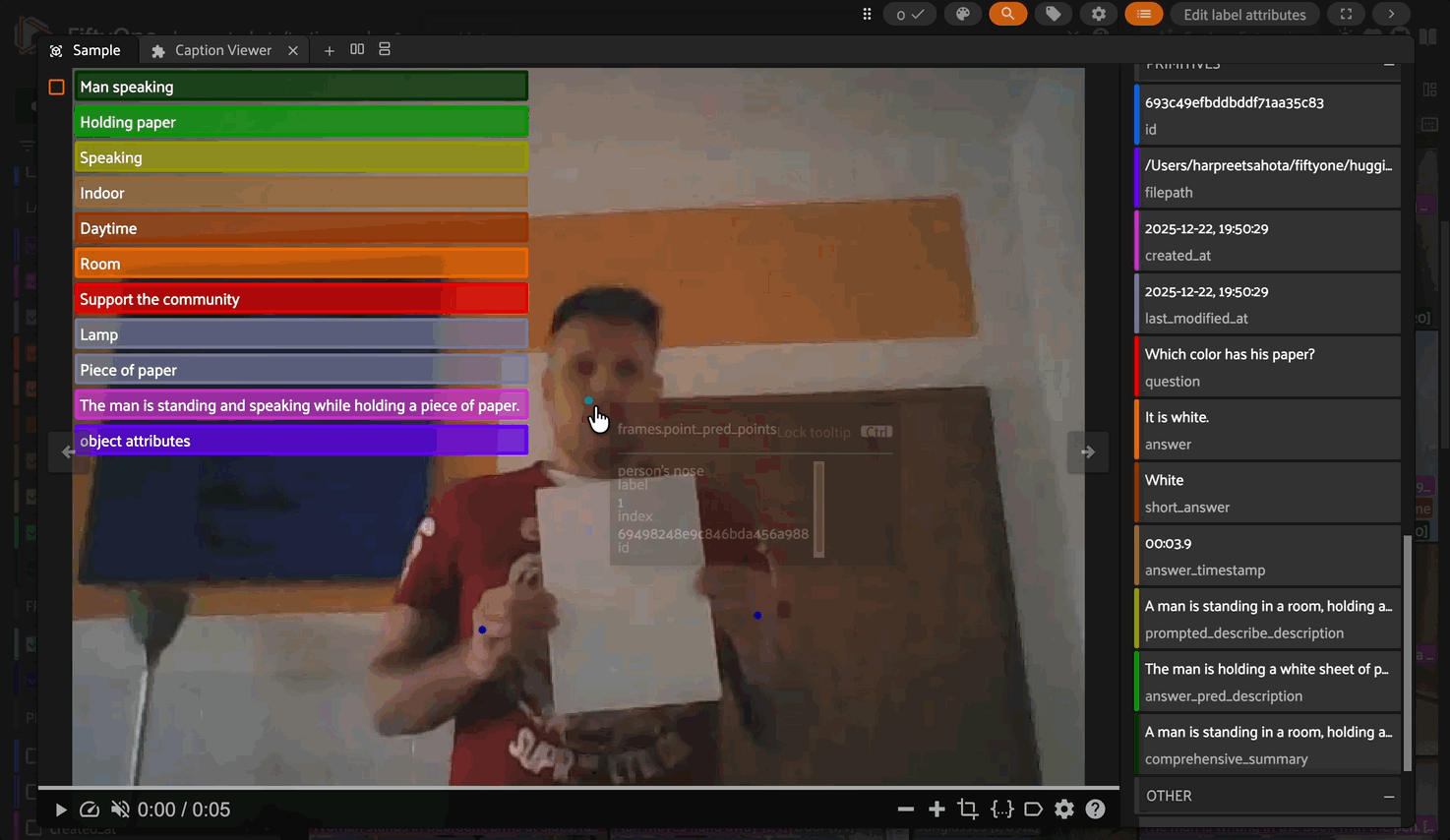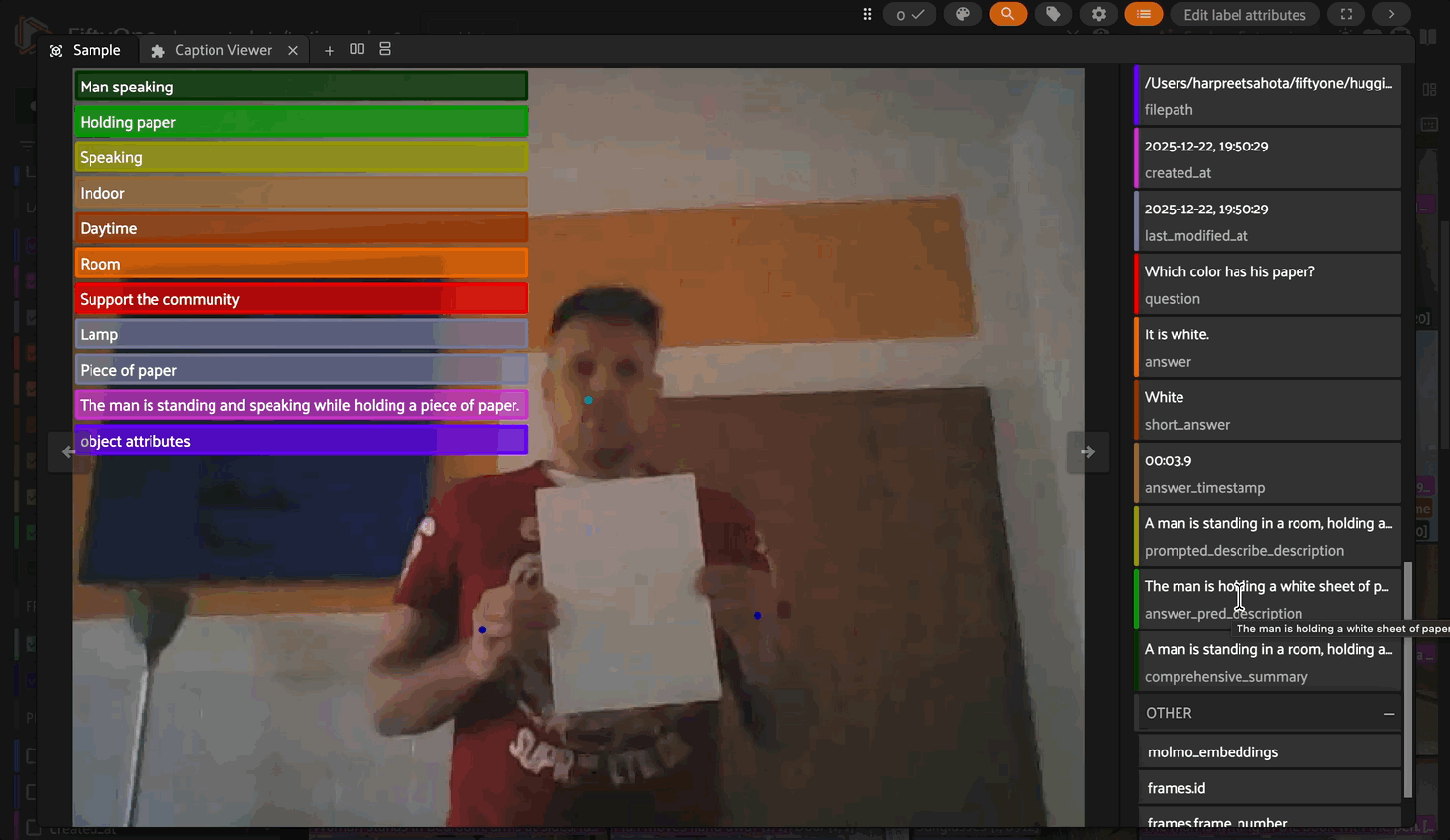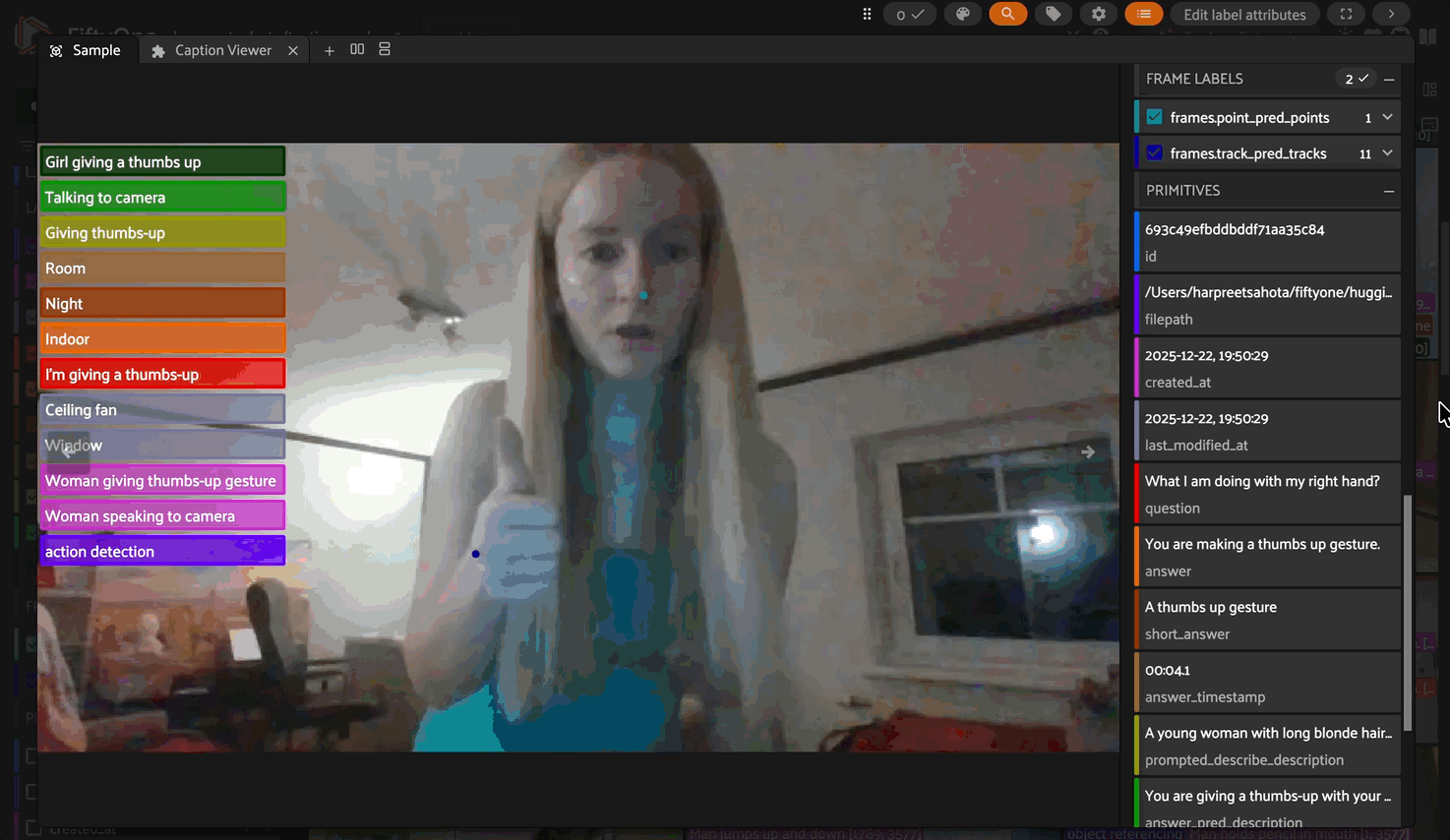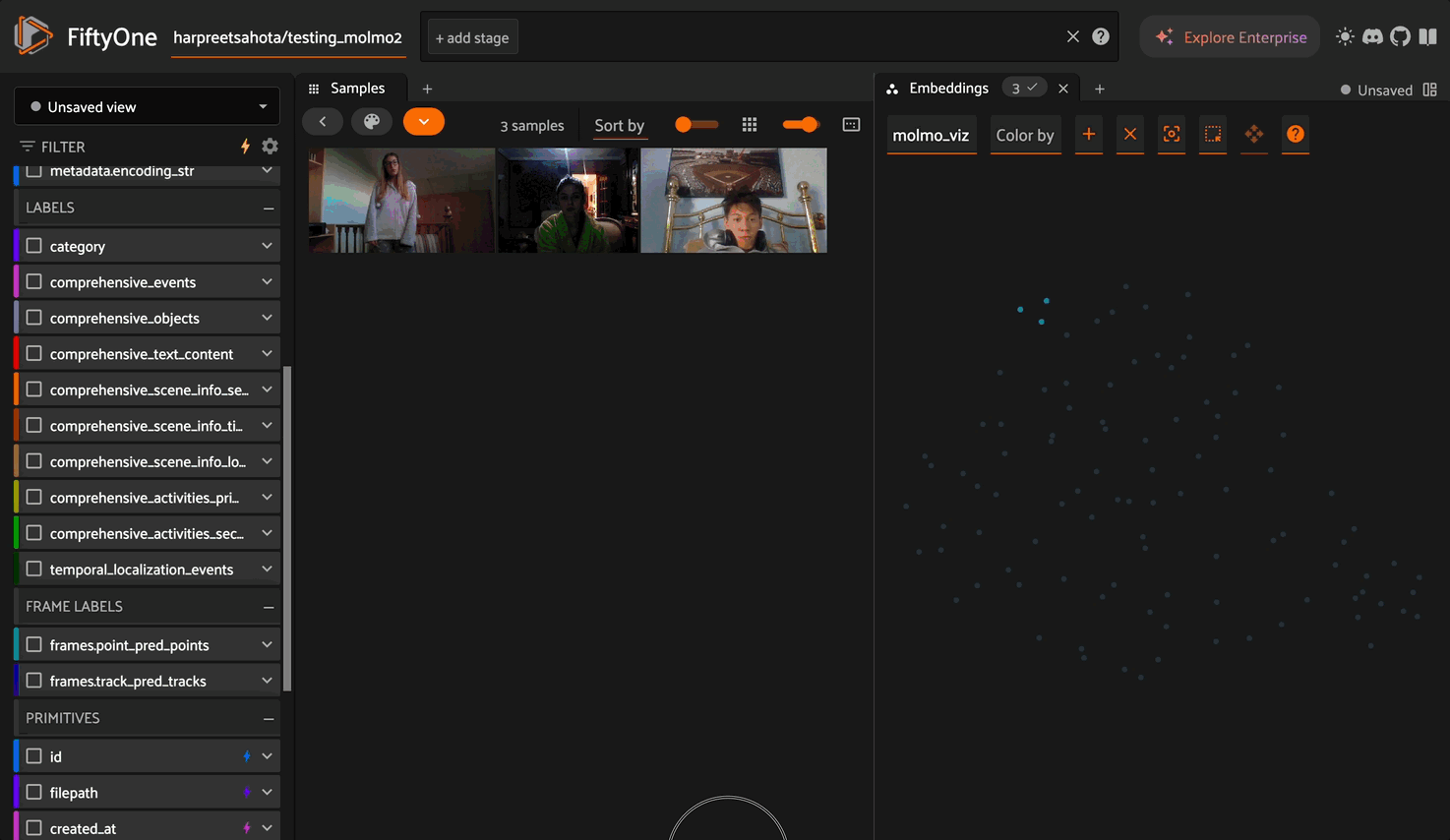
Pointing#
Point to objects in video frames. The model identifies where instances of the specified object appear across frames and returns their coordinates.
Added field: Frame-level fo.Keypoints on each frame where the object is detected. Each keypoint contains normalized (x, y) coordinates and an index identifying the object instance.
Tip: If pointing/counting is your primary use case, consider using
allenai/Molmo2-VideoPoint-4Bwhich is specifically finetuned for video pointing and counting tasks.
model.operation = "pointing"
model.prompt = "person's nose"
dataset.apply_model(
model,
"point_pred",
batch_size=16,
num_workers=1,
skip_failures=False
)
Tracking#
Track objects across video frames. Similar to pointing, but keypoints for the same object share an fo.Instance to link them across time.
Added field: Frame-level fo.Keypoints with fo.Instance linking. Objects maintain consistent identity across frames, enabling trajectory analysis.
model.operation = "tracking"
model.prompt = "person's hand"
dataset.apply_model(
model,
"track_pred",
batch_size=16,
num_workers=1,
skip_failures=False
)
Comprehensive#
Run a full video analysis that extracts multiple types of information: summary, events, objects, text content, scene info, and activities.
Added fields: Multiple fields are added to each sample:
comprehensive_summary— text descriptioncomprehensive_events—fo.TemporalDetectionsfor activities/eventscomprehensive_objects—fo.TemporalDetectionswith first/last appearance timescomprehensive_scene_info_*—fo.Classificationfields (setting, time_of_day, location_type)comprehensive_activities_*—fo.Classificationorfo.Classifications
model.operation = "comprehensive"
dataset.apply_model(
model,
"comprehensive",
batch_size=2,
num_workers=1,
skip_failures=False
)
Temporal Localization#
Find and localize activity events in the video with start/end timestamps.
Added field: fo.TemporalDetections on each sample containing detected events with their time intervals and descriptions.
model.operation = "temporal_localization"
dataset.apply_model(
model,
"temporal_localization",
batch_size=2,
num_workers=1,
skip_failures=False
)
Launch the App#
session = fo.launch_app(dataset, auto=False)
Citation#
If you use Molmo2 in your research, please cite the technical report:
@techreport{molmo2,
title={Molmo2: Open Weights and Data for Vision-Language Models with Video Understanding and Grounding},
author={Clark, Christopher and Zhang, Jieyu and Ma, Zixian and Park, Jae Sung and Salehi, Mohammadreza and Tripathi, Rohun and Lee, Sangho and Ren, Zhongzheng and Kim, Chris Dongjoo and Yang, Yinuo and Shao, Vincent and Yang, Yue and Huang, Weikai and Gao, Ziqi and Anderson, Taira and Zhang, Jianrui and Jain, Jitesh and Stoica, George and Han, Winston and Farhadi, Ali and Krishna, Ranjay},
institution={Allen Institute for AI},
year={2025}
}
